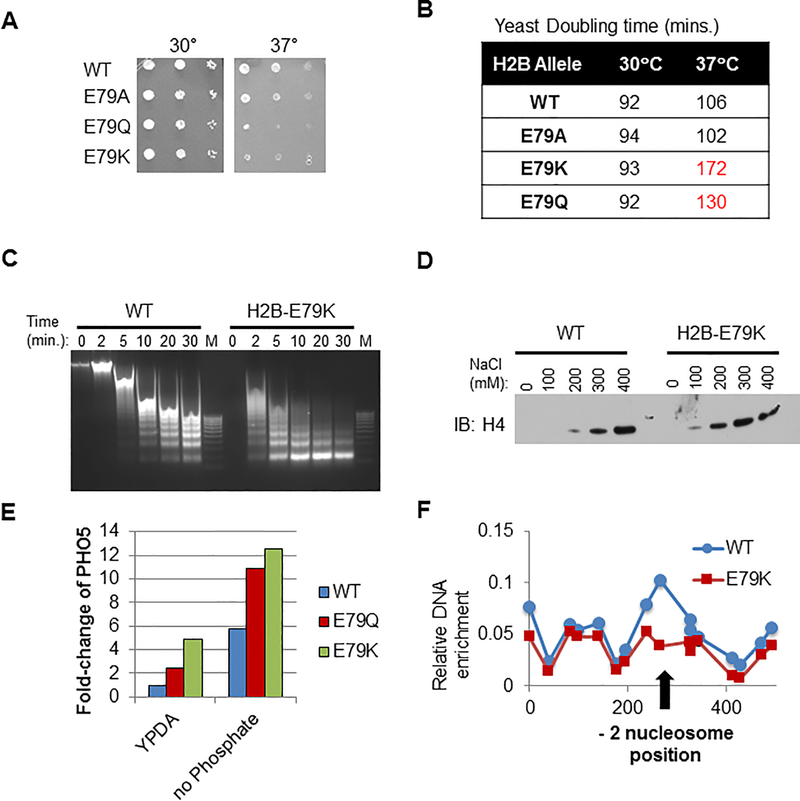
Figure 4. Expression of mutant H2B in yeast destabilizes nucleosomes, deregulates gene expression and reduces nucleosome occupancy at the PHO5 promoter.
WT or E79K H2B (analogous to human H2B-E76K) was expressed in S. Cerevisiae. (A) Yeast cells expressing H2B-E79K are temperature sensitive. Limiting dilutions of yeast expressing WT, E79A, E79Q or E79K were plated and incubated at 30°C or 37°C. Cell growth was evaluated after 1 day. (B) Yeast doubling time is significantly increased in cells expressing E79K-H2B at 37°C. (C) Time course of MNase sensitivity from spheroplasted yeast grown in rich media. M, marker. (D) Chromatin pellets were extracted with increasing concentrations of salt as indicated. Immuno-blotting of the soluble fraction was performed with antibody to H4. (E) Cells expressing WT, E79Q or E79K H2B were maintained in either rich media (YPDA) or phosphate-free media and expression of the phosphate-inducible PHO5 gene was measured by RT-PCR. (F) Nucleosome scanning assay of the PHO5 promoter from cells expressing either WT or E79K grown in rich media. Chromatin was digested with MNase, mononucleosomal DNA was purified and MNase protection was determined by qPCR. H2B occupancy at −2 nucleosome position of PHO5 is reduced in E79K cells as indicated by the arrow.