Figure 5.
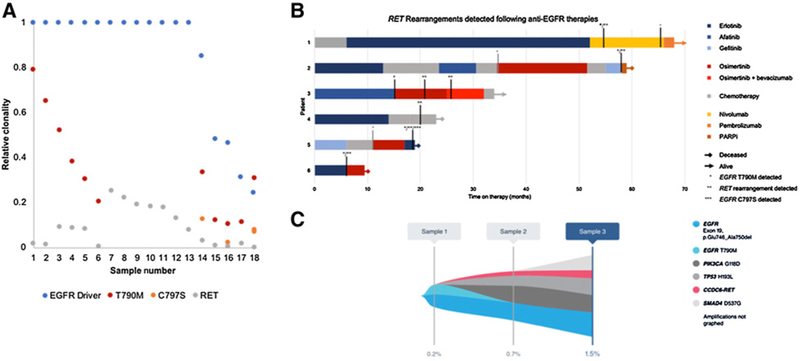
Landscape of genomic alterations found in the cfDNA of 15 patients with both an EGFR driver mutation (exon 19 deletion or L858R) and a RET fusion. A, Relative clonality of the EGFR driver mutation and RET fusion compared with on-target EGFR TKI mechanisms of resistance (T790M and C797S) among the 18 samples with RET fusion detected. B, Order and duration of systemic therapies among the 6 patients with both an EGFR driver mutation (exon 19 deletion or L858R) and a RET rearrangement detected in cfDNA and detailed clinical history available. EGFR TKIs are shown in shades of blue or red, chemotherapy (various) in gray, and other therapies in orange. Patients still living are indicated with an arrow, and time of death is indicated with a diamond. Vertical black lines indicate timing of the Guardant360 blood draw relative to treatment timing, and vertical gray lines indicate timing of other liquid biopsy or tissue molecular tests. The first detection of EGFR T790, the RET fusion, or EGFR C797S is indicated with a single, double, or tripleasterisk, respectively. C, Tumor response map for patient GH-003 showing suppression of EGFR T790M between sample 1 and sample2while the patient was on osimertinib, but emergence of RET fusion and alterations in PIK3CAand TP53.Treatment between samples2and 3 included addition of bevacizumab to osimertinib with relativelystable VAF of the RET fusion, PIK3CA, and TP53 alterations, but emergence of a SMAD4 alteration.
