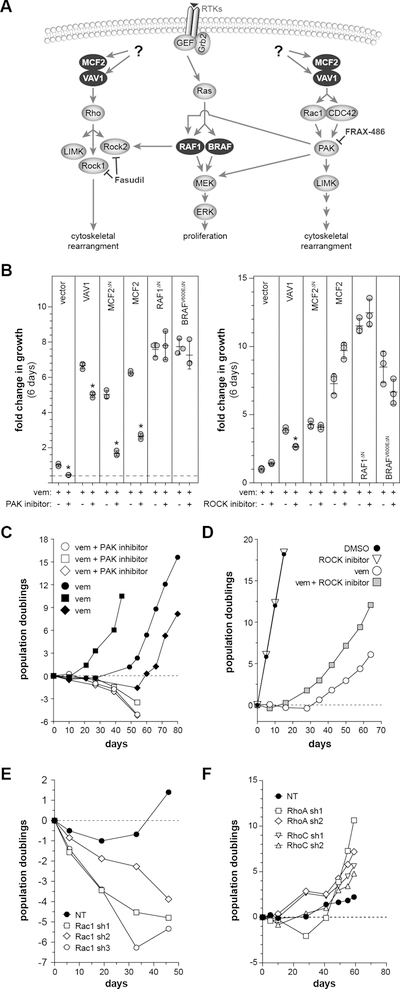
Figure 3. Evaluation of DBL GEF downstream signaling mechanism in A375 cells.
(A) DBL family members have exchange activity for members of the RHO and RAC1/CDC42 family, each having distinct signaling mechanisms. (B) The addition of the PAK inhibitor FRAX-486 (50 nM) is able to reduce vemurafenib resistance driven by MCF2 and VAV1. However, the ROCK inhibitor Fasudil did not show a consistent effect [*adjusted p < 0.001 relative to vemurafenib alone]. (C) Long-term treatment of A375 cells with a PAK inhibitor (FRAX-486) is capable of converting vemurafenib-induced cytostasis to cell killing, while long-term treatment with a ROCK inhibitor (Fasudil) (D) shows a trend of enhanced growth in vemurafenib. (E) Knockdown of RAC1 using three independent shRNAs converts vemurafenib-induced cytostasis to cell killing in long-term cultures of A375, while knockdown of either RHOA or RHOC does not impact cell growth with long-term vemurafenib treatment (F).