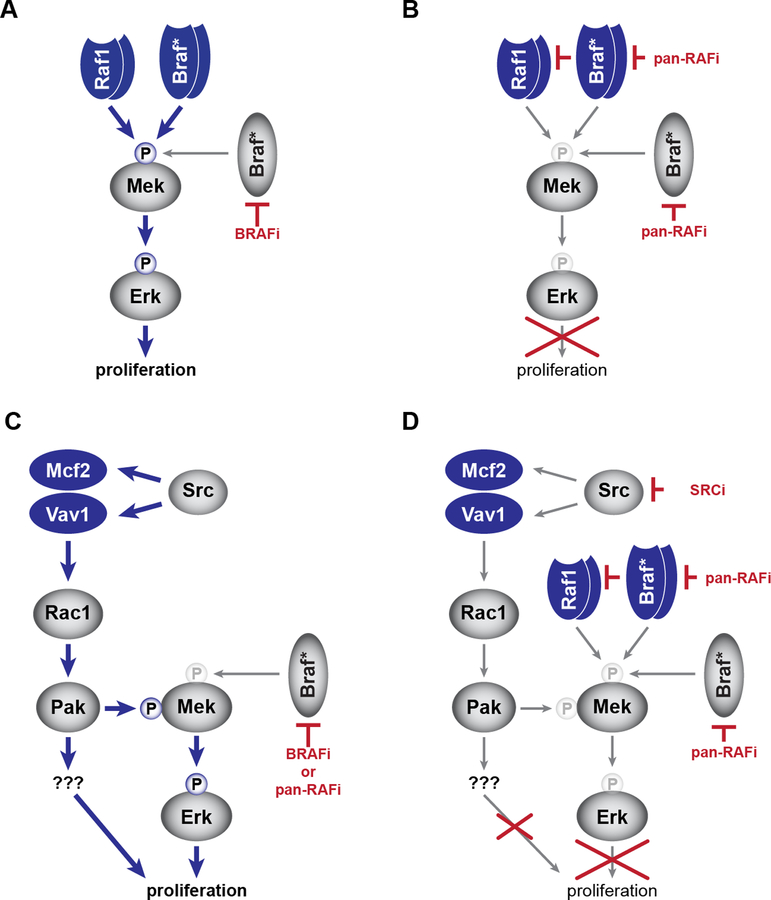
Figure 7. Model of drug resistance mechanisms.
We have shown that N-terminal truncation of either RAF1 or BRAFV600E leads to vemurafenib resistance (A) that can be overcome with a pan-RAF inhibitor (e.g. LY3009120) (B). Our genetic screen identified a DBL-RAC1-PAK resistance mechanism that can drive proliferation in the presence of either BRAF inhibitor (e.g. vemurafenib) or a pan-RAF inhibitor (C). However, the combination of a SRC inhibitor (e.g. saracatinib) and a pan-RAF inhibitor can block both mechanisms identified by our screen (D).