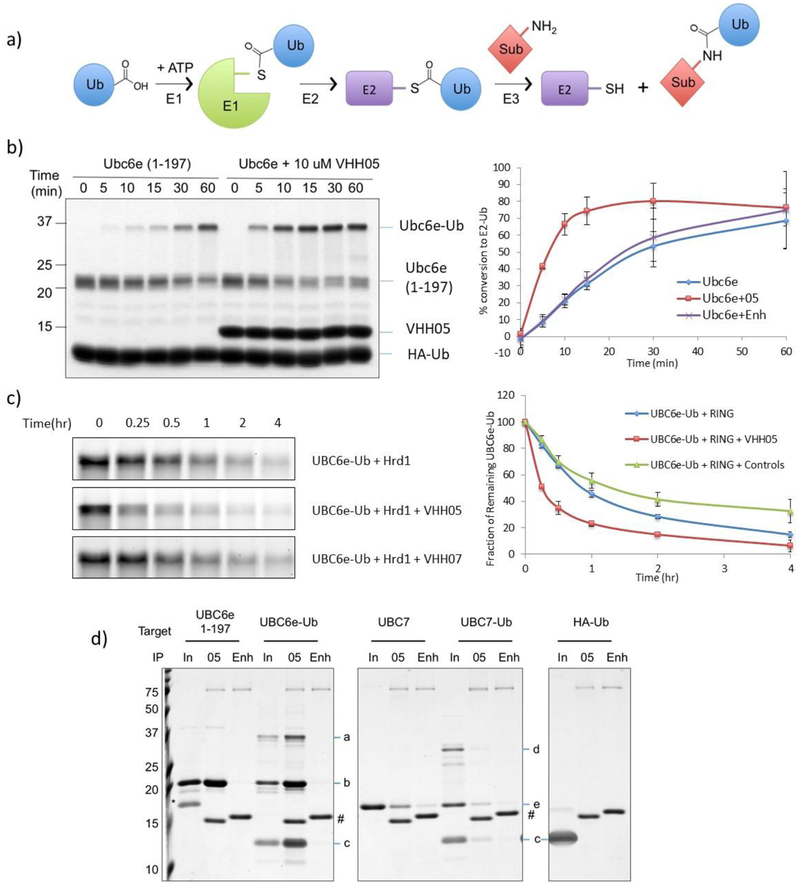
Figure 2.
VHH05 accelerates the enzymatic activity of UBC6e. (a) Schematic representation of ubiquitin pathway. (b) VHH05 accelerates the E2-loading of UBC6e. Ubiquitination reactions were quenched at the indicated time by addition of SDS-containing sample buffer and resolved by SDS-PAGE on a 15% non-reducing gel (left) and quantified by densitometry (right). Data points represent mean ± standard deviation. (c) VHH05, but not an MHC-II specific VHH (VHH07), accelerates the hydrolysis of UBC6e-Ub. Samples were prepared and analyzed as in panel b. (d) VHH05 binds to both UBC6e and UBC6e-Ub. E2, E2-Ub thioester conjugates or HA-Ub were diluted using tris buffered saline and immunoprecipitated with VHH05- or enhancer-conjugated sepharose beads as described in the methods section. Samples were eluted in 4% SDS with 100 mM dithiothreitol and resolved with 15% SDS-PAGE. Since elution was carried out with DTT the thioester has been partially hydrolyzed. For IP labels “in” indicates input; “05” indicates VHH05 immunoprecipitation; “Enh” indicates enhancer immunoprecipitation. a: UBC6e(1-197)-Ub. b: UBC6e(1-197). c: HA-Ub. d: UBC7-UB. e: UBC7. *: SUMO. #: VHH05 and VHH enhancer.