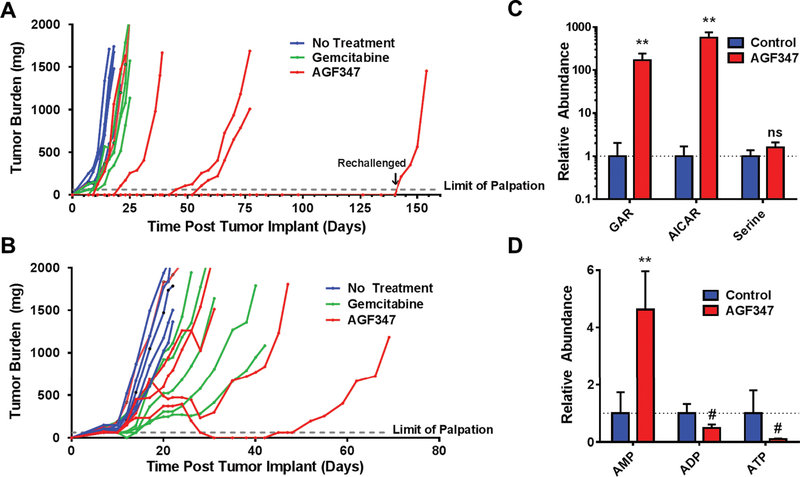
Figure 5. In vivo efficacy in early stage and upstage trials and pharmacodynamics of AGF347 toward MIA PaCa-2 PaC xenografts.
A: Female NCr SCID mice (11 weeks old 20.2 g average body weight) were implanted bilaterally with human MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer xenograft fragments. Treatment was initiated on day 1 following SC tumor implantation. The mice were dosed as follows: AGF347, Q2dx8 at 15 mg/kg/injection, total dose 120 mg/kg; and GEM, Q4dx4 at 120 mg/kg/IV injection, total dose 480 mg/kg. Results are shown for individual mice. B: Female ICR SCID mice (10 weeks old; 19 g average body weight) were implanted bilaterally with human MIA PaCa-2 PaC tumors. On day 7 following SC implantation, the mice were dosed as for A. C,D: Targeted metabolomics on tumor samples from upstage trial mice. GAR, AICAR, and serine (C) and adenine nucleotides (AMP, ADP, ATP) (D) were quantified in control and AGF347-treated mice. Results for metabolomics (mean ± standard deviation) are normalized to control values and represent one tumor each taken from three different control and AGF347-treated mice. The changes in GAR and AICAR were statistically significant (**, p < 0.01) as were the changes in adenine nucleotides (**, p<0.01, #, p < 0.1) while the changes in serine did not reach statistical significance (“ns”= not significant), likely due to circulating serine pools.