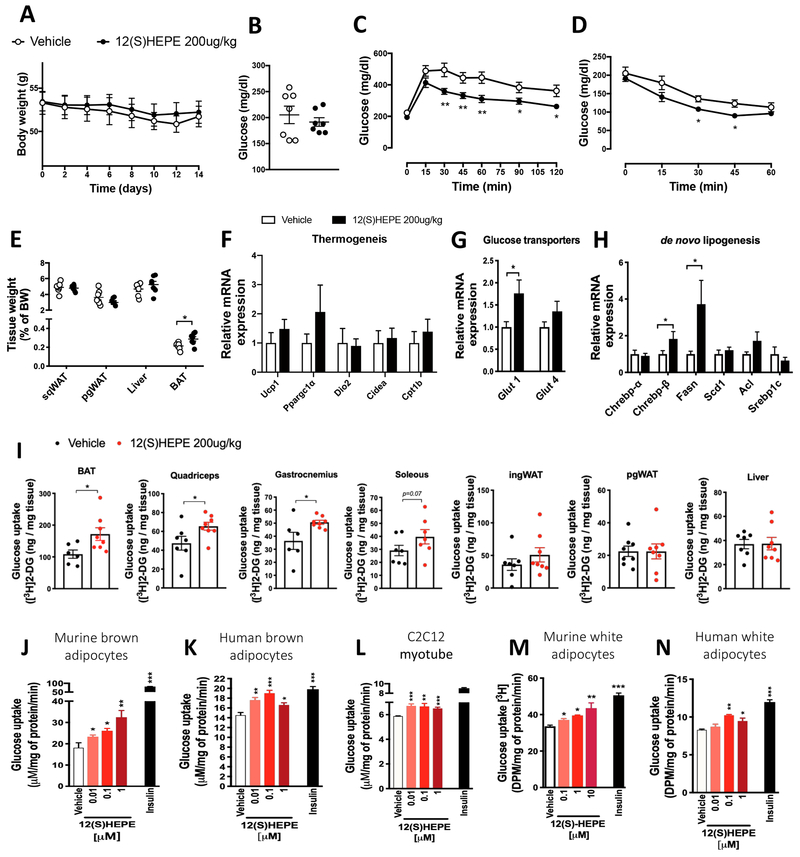
Figure 6: 12-HEPE serves as a glucose uptake mediator.
A) Body weight in 12(S)-HEPE and Vehicle treated DIO male mice (n = 7).
B) Fasting serum glucose measured in 12(S)-HEPE and Vehicle treated DIO mice (n = 7).
C) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) performed in 6h fasted 12(S)-HEPE and Vehicle treated DIO mice. (n = 7).
D) Glycemia during the insulin tolerance test (ITT) performed in 6h fasted 12(S)-HEPE and Vehicle treated DIO mice (n = 7).
E) Ratio of tissue weight to body weight calculated for pgWAT, ingWAT, liver and BAT harvested from 12(S)-HEPE and Vehicle treated DIO mice (n = 7).
F-H) mRNA expression measured by qPCR of genes associated with the thermogenic program associated, glucose transport and de novo lipogenesis in BAT from 12(S)-HEPE and Vehicle treated DIO mice (n = 7).
I) Glucose uptake into BAT, ingWAT, pgWAT, quadriceps, gastrocnemius, soleus and liver of C57BL6/J lean mice i.v. injected with 12(S)-HEPE or vehicle, 30 minutes before an [3H]2-deoxyglucose i.v. injection (n = 6-8).
J-N) In vitro glucose uptake into murine brown adipocytes, human brown adipocytes, murine myocytes (C2C12), murine white adipocytes (3T3-F442A cells) and human white adipocytes (hWAT) treated with 12(S)-HEPE or vehicle for 30 minutes before adding [3H]2-deoxyglucose. (n = 4-6 experimental replicates from at least 2 biological replicates). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. See also Figure S6.