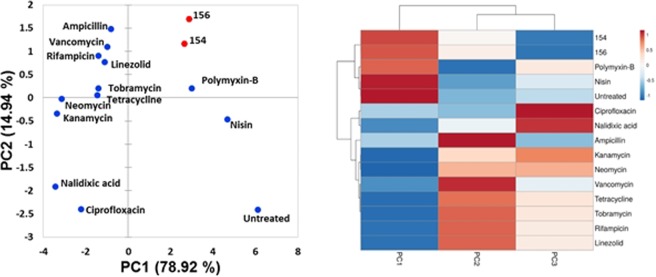
Figure 4.
2D Principal component analysis of antibiotic-treated B. subtilis 6051 using unweighted variables from cytological imaging with associated agglomerative hierarchical clustering and heat map made in ClustVis47. PCA demonstrates DPA 154 and 156 induce morphology resembling membrane-active compounds polymyxin-B and nisin. Three independent wells of bacteria were treated with each antibiotic and 4 fields/well were imaged and the corresponding segmentation metrics were averaged. DPA compounds (154 and 156) appear to be more closely related to membrane active compounds polymyxin-B and nisin than DNA synthesis inhibitors such as ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid. Principal components (PC) are the variable reduction outputs of the PCA algorithm that contribute a percentage of the variation of a sample; PC1 (78.92%) vs PC2 (14.94%). Variables that contribute to each principal component/factor are summarized in the supplemental figures (Table S8, Figs S3 and S4, Tables S12 and S13). A list of antibiotics and mechanisms of action used for cytological profiling may be found in Table S6. Definitions of select measures used in cytological profiling may be found in Table S9.