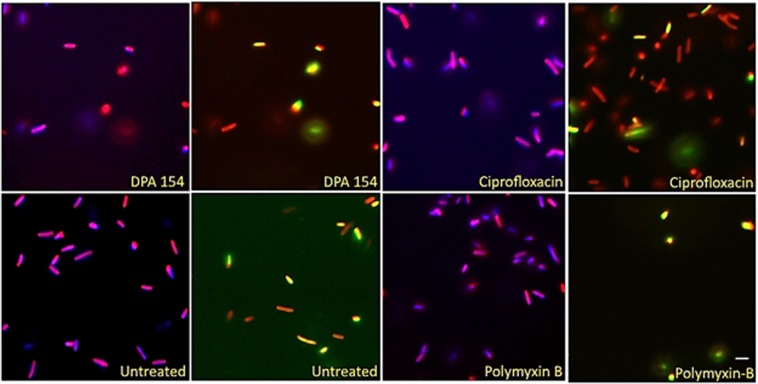
Figure 9.
Comparison of E. coli treated with DPA 154, ciprofloxacin, and polymyxin-B. DPA 154 causes induction of spheroplastic phenotype like polymyxin-B and diminished nuclear morphology consistent with ciprofloxacin. Presence of features of both morphologies provides evidence for a dual mechanism of action for DPA 154. E. coli stained with DAPI (blue) FM4-64 (red) and SytoxG (green) and treated with DPA 154, ciprofloxacin, and polymyxin-B demonstrating membrane permeating effects of DPA 154. DPA 154 induces a high rate of smaller, rounded, SytoxG permeated cells consistent with membrane permeating antibiotics. Ciprofloxacin induces a longer, filamentous phenotype and cells with fewer membrane disruptions as compared to polymyxin-B which induced a majority of small, rounded, membrane permeated cells. Scale bar 1 µm.