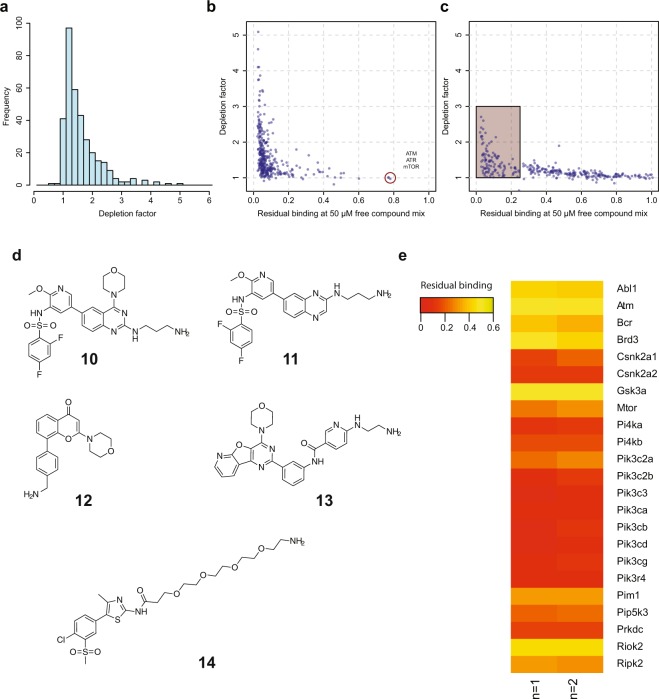
Figure 2.
Characterization of binding, depletion and competition properties of the new kinobeads mix. (a) Distribution of depletion factors for all identified kinases from an experiment using a lysate mix consisting of K562, HEK293 and human placenta shows that majority of kinases are only weakly depleted. (depletion factor F = 1 + [B]/KdB, with [B] indicating the bead ligand concentration and KdB being the respective dissociation constant). (b) Scatterplot displaying residual binding of all identified kinases on the beads when 50 µM free compound mix was present versus the depletion factor for kinases. Target proteins should ideally be in the left corner. Kinases in the right corner (red circle), which are neither depleted nor competed, bound unspecifically to the matrix. (c) Same plot as in b but for all non-kinase proteins. Square indicates non-kinase proteins with less than 25% residual binding at 50 µM free compound mix. (d) Compounds used for the lipid kinobeads. (e) Heatmap displaying residual binding for all kinases captured with the lipid kinobeads (n = 2, see also Supplementary Table 4).