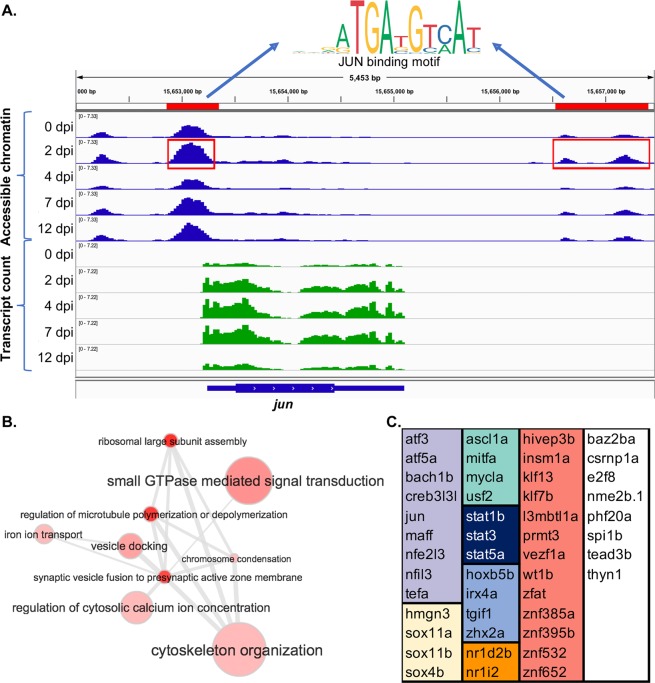
Figure 5.
Jun is a potential regulatory target of regeneration-associated promoters and enhancers. (A) IGV browser screenshot displaying accessible chromatin sequence pileups (blue) and expressed sequence pileups (green) surrounding jun gene at 0, 2, 4, 7, and 12 dpi. Red bars and boxes indicate sequence determined to be differentially open at 2 dpi compared to control (0 dpi). Motif finding of sequences highlighted in red identified motifs corresponding to the JUN binding site. (B) Gene ontology (GO) analysis of inferred targets of JUN suggests roles in calcium regulation, microtubule dynamics, and translation. GO terms corresponding to JUN target genes were summarized, clustered and visualized using REVIGO58. Node size corresponds to GO term frequency. Similar GO terms are linked by edges whose thickness corresponds to degree of similarity. (C) Inferred targets of JUN include 47 regeneration-associated TF genes. TF genes are grouped by transcription factor family: violet, leucine zipper; yellow, HMG/sox; green, helix-loop-helix; dark blue, STAT; light blue, hox; orange, nuclear receptor; red, C2H2 zinc finger; white, includes members of the AT hook, E2F, Ets, MBD, and TEA families as well as factors with uncategorized DNA binding domains.