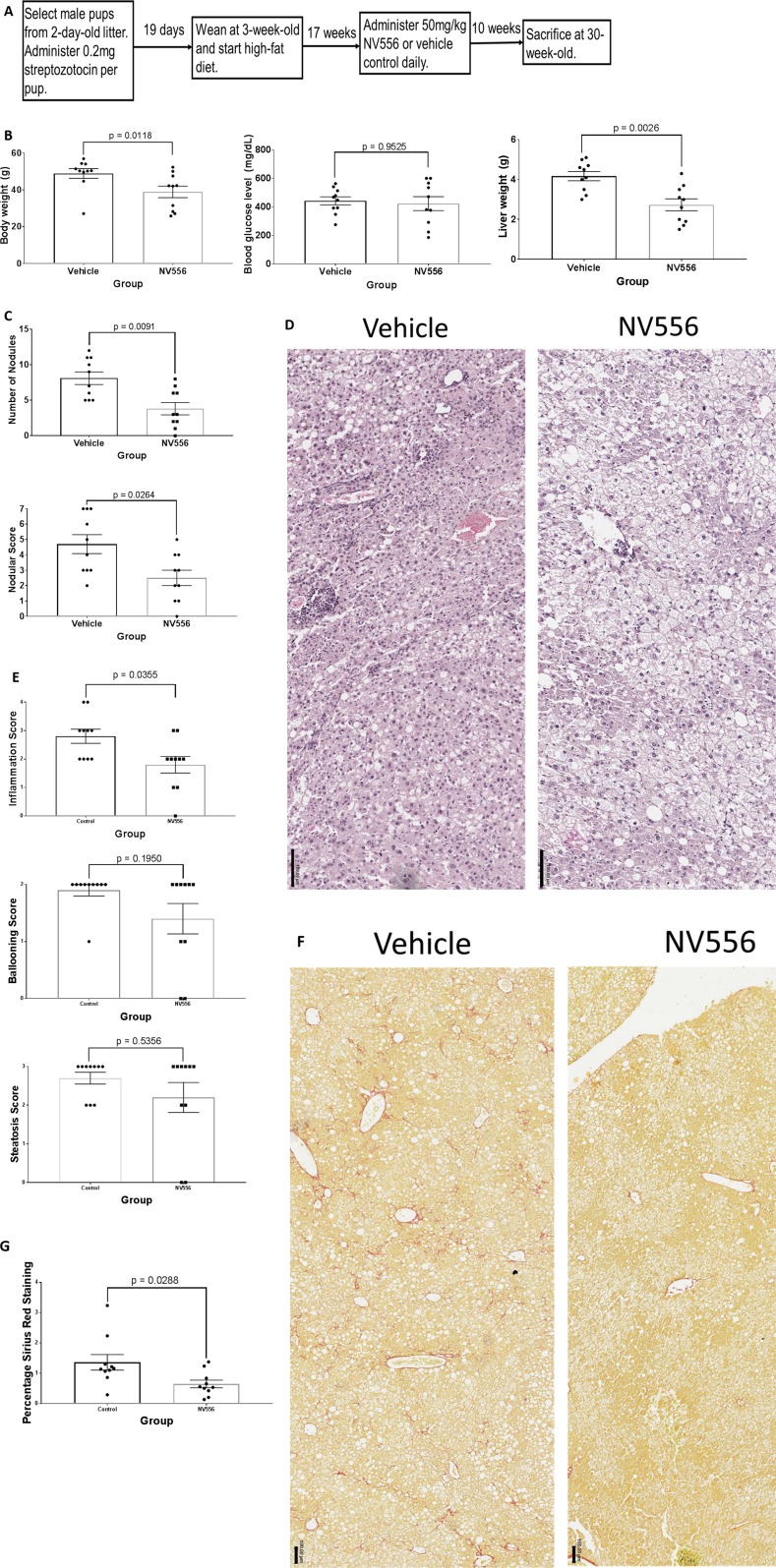
Figure 3.
NV556 decreased body weight, liver weight, tumor burden, inflammation, and fibrosis in mice with NASH-induced HCC. (A) Flowchart for studies on HCC. HCC was induced in male C57BL/6J mice by intraperitoneal injection of 200 µg of STZ 2 days after birth followed by a free-feeding high-fat diet (60% kcal fat) after 3 weeks of age for 27 weeks. Fifty mg/kg NV556 or vehicle control was administered via oral gavage daily to mice for 70 days before sacrifice at 30 weeks of age. (B) Body weight (left), blood glucose level (middle), and liver weight (right) of mice. (C) Number of detectable nodules (left) and nodular scoring for tumor burden (right) in livers of mice. (D) H&E staining on paraffin-embedded liver sections. Bar indicates 50μm. (E) Inflammation, steatosis, and ballooning scoring on H&E stained tissues. (F) Liver fibrosis identified by Sirius red staining (left) and quantified by ImageJ (right). Bar indicates 100μm. (G) Percentage of Sirius Red staining. All error bars indicate ± standard error from the mean, with p-values from two-tailed Mann-Whitney test.