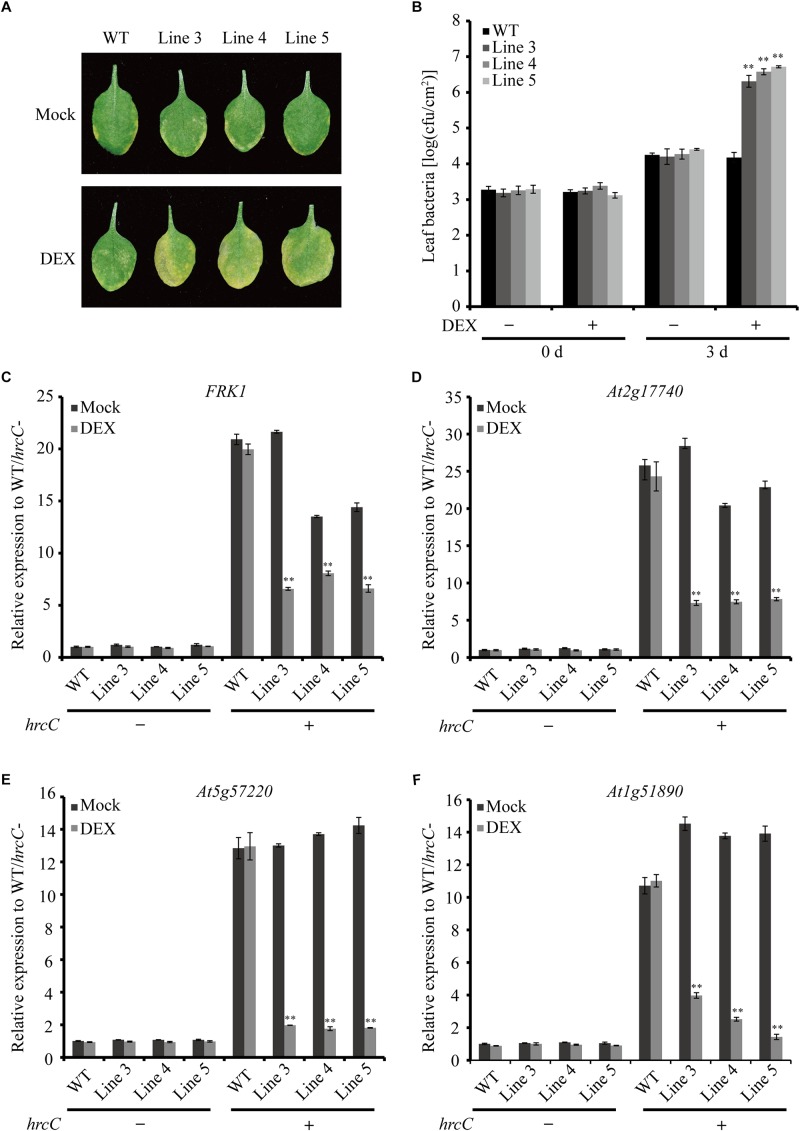
FIGURE 5.
Heterologous expression of AGLIP1 suppresses PTI signaling and promotes disease development in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. (A) Disease symptoms in the wild-type and AGLIP1 transgenic Arabidopsis plant lines after inoculation with bacterial pathogens Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) DC3000 hrcC mutant. Disease symptoms exhibited on the leaves of the wild-type and AGLIP1 transgenic lines Line 3, Line 4 and Line 5 with mock or DEX treatment after pressure infiltration with the Pst DC3000 hrcC mutant. Photos were taken at 3 days after inoculation. (B) In planta bacterial population of Pst DC3000 hrcC mutant in the wild-type and AGLIP1 transgenic lines at 0 day and 3 days after inoculation. (C–F) Upregulation of the defense marker genes FRK1, At2g17740, At5g57220, and At1g51890, respectively, induced by Pst DC3000 hrcC mutant were completely inhibited in transgenic Line 3, Line 4 and Line 5 after DEX-induced expression of AGLIP1. The 4–5 weeks transgenic plant were treated with 30 μM DEX or 0.1% ethanol as mock control for 24 h, followed by the spray inoculation of Pst DC3000 hrcC mutant for 6 h. The expression level of AtUBQ5 was used as an internal reference for normalizing within the samples. Asterisks (∗∗) indicate P value < 0.01; means ± standard error are shown.