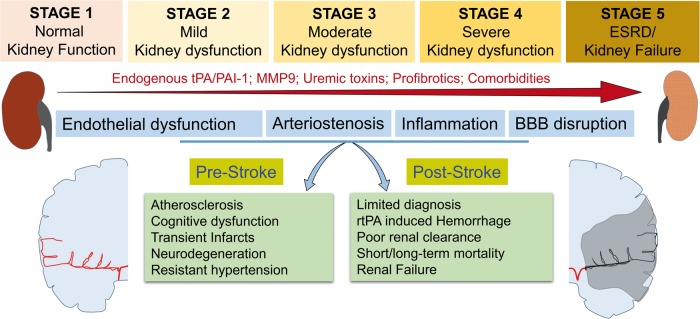
Figure 1.
CKD induces pre- and post-stroke complications. Abnormal changes in endogenous tPA/PAI-1, MMP-9, uremic toxins such as indoxyl sulfate, p-cresyl sulfate and guanidino substances and profibrotics like TGF-β1, Tenascin-C, PAI, ANG-II, and comorbid conditions like hypertension and diabetes lead to the progression of CKD from stage 1 to stage 5. Advancement of CKD also leads to progressive endothelial dysfunction, vascular stiffness, BBB disruption, and peripheral/central inflammation. These have severe consequences in the brain during both pre-stroke and post-stroke stages.
tPA: tissue plasminogen activator; PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase-9; ESRD: end-stage renal disease; BBB: blood–brain barrier; rtPA: recombinant tissue plasminogen activator.