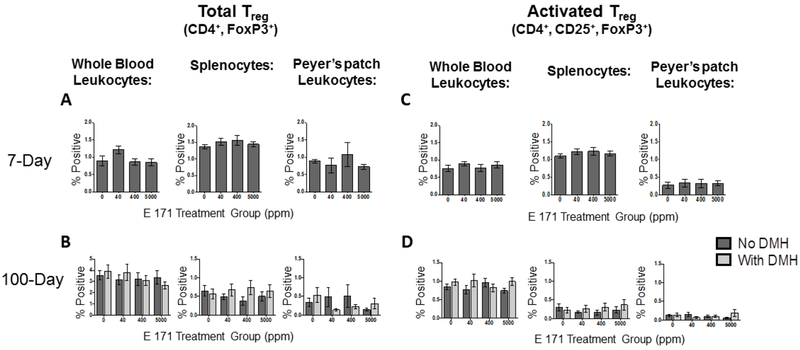
Figure 3. Acute or chronic exposure to dietary E 171 did not significantly affect the frequency of circulating or GI-resident Tregulatory (Treg) cells.
The frequency of gut resident and circulating total and activated Treg cells were determined in rats fed dietary E 171 for a total of 7 or 100 days. Rats in the 100 day study were pretreated with 180 mg/kg of DMH or Vh control by i.p. injection. Following the 7- and 100-day feeding period, animals were euthanized and PBMC, spleen, and Peyer’s patches were collected and processed into single cell suspensions. Cells were then surface stained for CD4 and CD25 and subsequently stained intracellularly for FoxP3. Following antibody stains, cells were analyzed via flow cytometry to identify Treg cell populations. Data are presented as a percentage of the live cells falling in the lymphocyte gate. Total Treg from 7 (A) and 100 (C) as well as activated Treg from 7 (B) and 100 (D) day studies are shown. Data were analyzed for statistical significance using a one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test when there were no significant differences in the variance of the standard deviation.