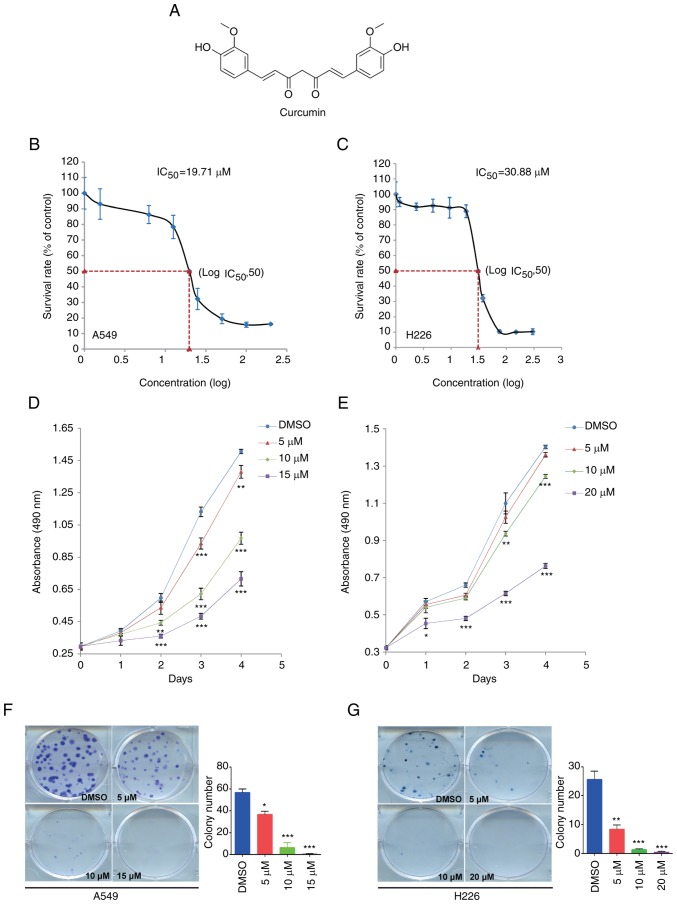
Figure 1.
Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation in NSCLC cell lines. (A) Chemical structure and formula of curcumin. (B) A549 and (C) H226 cells were treated with serial concentrations of curcumin for 72 h. An MTS assay was used to determine the proliferation of A549 and H226 cells. (D) A549 and (E) H226 cells were cultured with different doses of curcumin, and an MTS assay was used to detect cell proliferation at the same time point each day. (F and G) Colony formation assay indicated that curcumin significantly inhibited colony formation in (F) A549 and (G) H226 cells. Cells were treated with various doses of curcumin and colonies were counted after 2 weeks (A549) or 3 weeks (H226) using Giemsa staining. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. the DMSO group. IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration.