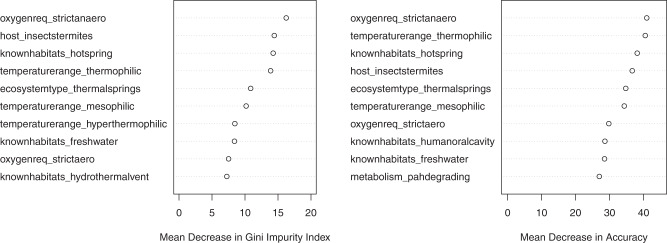
Fig. 3.
Importance of top ten predictors in the RF model of CRISPR incidence using the ProTraits predictors. The mean decrease in accuracy measures the reduction in model accuracy when a variable is randomly permuted in the dataset. The Gini impurity index is a common score used to measure the performance of decision-tree based models (e.g. RF models). Briefly, when a decision tree is built the Gini impurity index measures how well separated the different classes of outcome variable are at the terminal nodes of the tree (i.e., how “pure” each of the nodes is). The mean decrease in Gini impurity measures the estimated reduction in impurity (increase in purity) when a given variable is added to the model. These importance scores are useful to rank variables as candidates for further study, but in themselves should not be taken as statistical support or effect sizes similar to those seen in linear regression. RF models may include non-linear combinations of variables, and therefore the contribution of any one variable is not as easily interpreted as with a linear model, a drawback of this approach. See Fig. S7 for all predictor importances