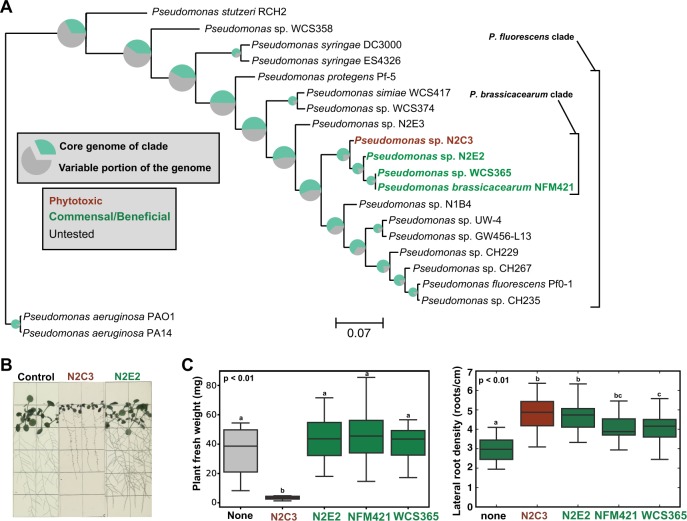
Fig. 1.
A pathogen within a clade of beneficial Pseudomonas spp. a A species tree of characterized Pseudomonas strains was generated using 217 conserved housekeeping genes. Strain names are color-coded to reflect plant-associated lifestyles based on their effects on Arabidopsis. Pie charts at each node reflect the proportion of the genome that encodes “core” genes that are present in each member of the clade, showing that there can be large differences in gene content over short evolutionary distances. b Gnotobiotic Arabidopsis seedlings inoculated with N2C3, N2E2, or a buffer control. c Fresh weight of seedlings treated with 10 mM MgSO4, N2C3, N2E2, NFM421, and WCS365. Lateral root density of seedlings treated with 10 mM MgSO4, N2E2, NFM421, and WCS365. Lower-case letters indicate statistically significantly different (p < 0.01, 26 > n > 12) means as determined by a two-sided Student’s T-test for unpaired samples. Boxplots are quartile plots of the observed data. Data shown are from one of two independent experiments performed with similar results