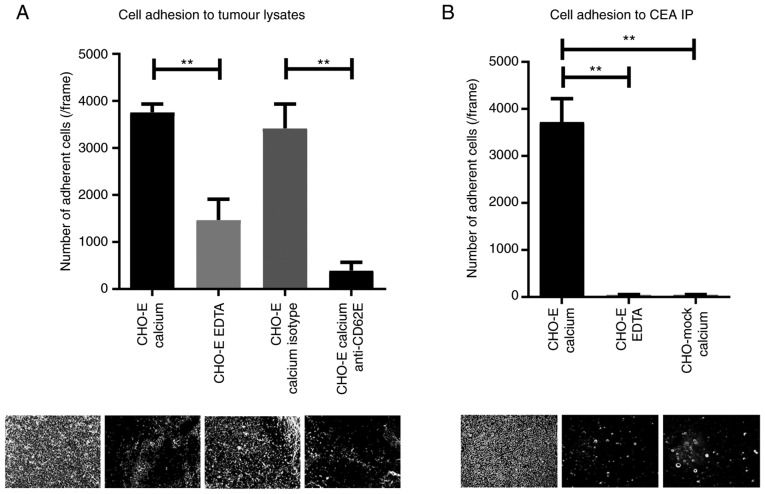
Figure 6.
CEA glycoprotein is a functional E-selectin ligand in NSCLC. (A) Adhesion of E-selectin-expressing cells to NSCLC lysates. Lysates of NSCLC tissue, derived from patient 7, were spotted on glass slides, and the adhesion of CHO-E cells was tested using a modified Stamper-Woodruff binding assay test. As E-selectin interactions are calcium-dependent, CHO-E cells were resuspended in calcium buffer. EDTA buffer was used as a control. Cells were pre-incubated with 20 µg/ml of specific mAbs prior to the adhesion experiment; isotype control or function-blocking anti-E-selectin mAb. (B) Adhesion of E-selectin-expressing cells to CEA immunoprecipitate. CEA was immunoprecipitated from NSCLC tissue derived from patient 7 and spotted on glass slides. Adhesion of CHO-E or CHO-mock cells to CEA IP was tested using a modified Stamper-Woodruff binding assay. CHO-E and CHO-mock cells were resus-pended in calcium buffer, and CHO-E cells resuspended in EDTA buffer were used as a negative control. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test was used for analysis. **P<0.01. Representative pictures captured for each condition (magnification, ×100) are represented below the respective graphs. CD62E, E-selectin; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; CHO, Chinese hamster ovary cells; CHO-E, E-selectin-expressing CHO; CHO-mock, empty vector-transfected CHO; isotype, isotype control Ab; mAb, monoclonal antibody.