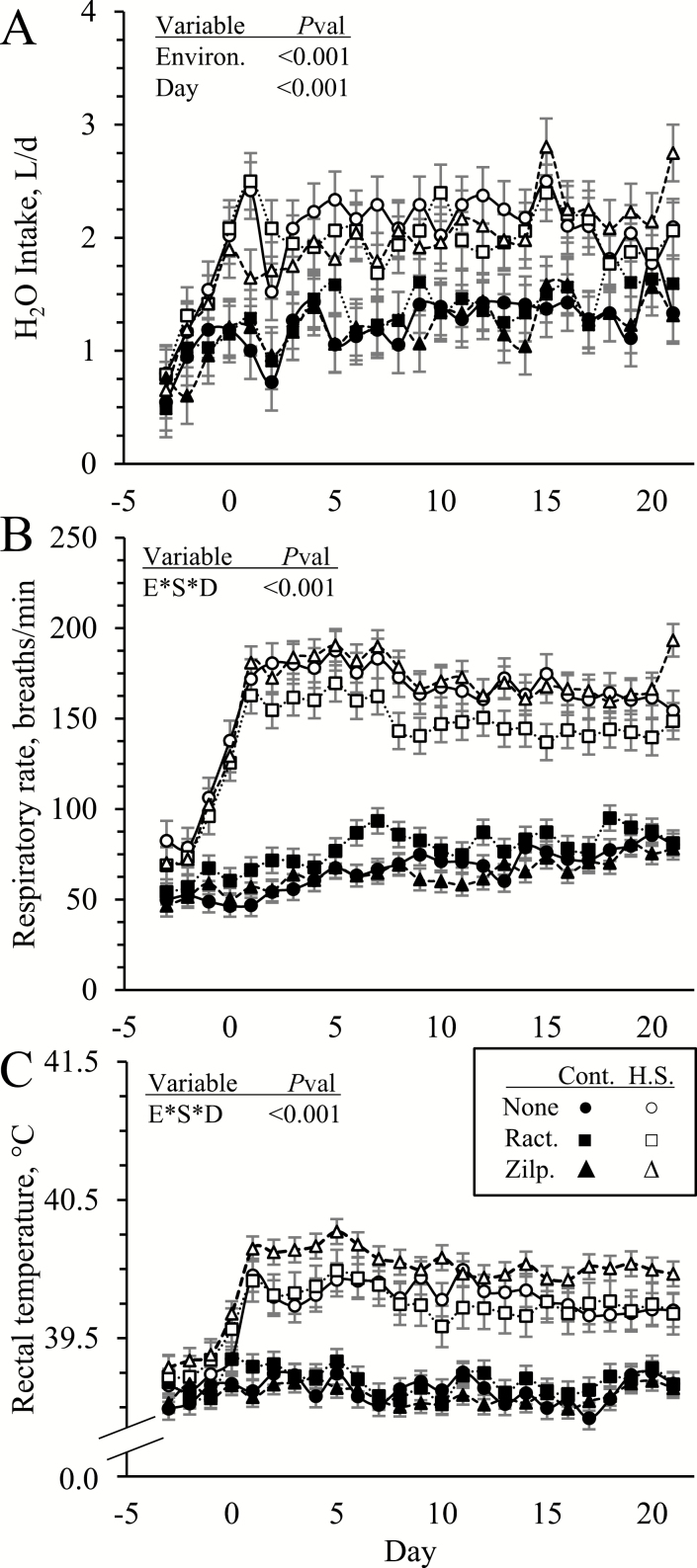
Figure 2.
Average daily H2O intake (A), respiratory rates (B), and rectal temperatures (C) in heat-stressed lambs fed concentrate diets supplemented with ractopamine or zilpaterol for 21 d. Lambs were fed in a 2 × 3 factorial: Cont./None, unsupplemented controls (n = 9); Cont./Ract., controls supplemented with 0.03996 g/d ractopamine HCl (n = 8); Cont./Zilp., controls supplemented with 0.025 g/d zilpaterol HCl (n = 8); H.S./None, unsupplemented heat-stressed lambs (n = 8); H.S./Ract., heat-stressed lambs supplemented with ractopamine HCl (n = 8); H.S./Zilp., heat-stressed lambs supplemented with zilpaterol (n = 8). Effects of environmental condition (Environ.), dietary supplement (Suppl.), day, and the interaction (E*S*D) are noted when significant (P < 0.05).