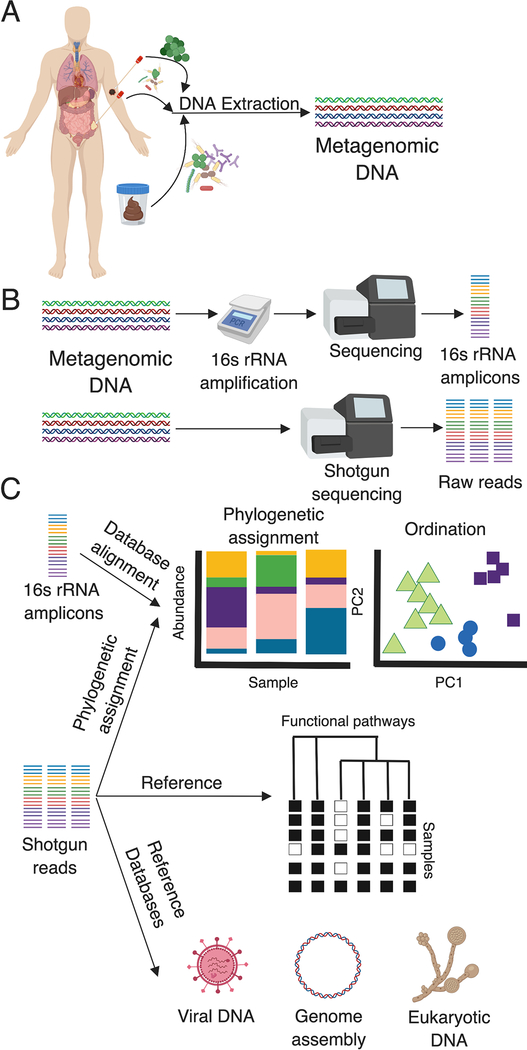
Figure 1. Schematic for metagenomic analysis.
A) The first step in microbiome analysis is selecting the sample, obtaining it with sterile technique, and preserving it with consideration of DNAses and RNAses. Samples can be obtained directly from tumors, skin, or fecal samples. DNA extraction via phenol chloroform or commercially available kits yields metagenomic DNA. B) The 16S rRNA gene can be amplified and sequenced. Alternatively, metagenomic DNA can be shotgun sequenced to yield DNA fragments of varying sizes. C) 16S rRNA reads can be computationally processed with publicly available pipelines yielding relative abundance of taxa per sample. Ordination methods such as PCA and PCoA are utilized to identify similarities and differences in diversity metrics (alpha, beta, gamma) between samples or between groups. Reads from metagenomic shotgun sequencing can be processed to yield the same information. In addition to taxonomy, shotgun reads can be processed and mapped to databases to determine functional pathways, assemble bacterial genomes, and understand the presence of viral or eukaryotic DNA depending on appropriate sequencing depth. Created with BioRender.