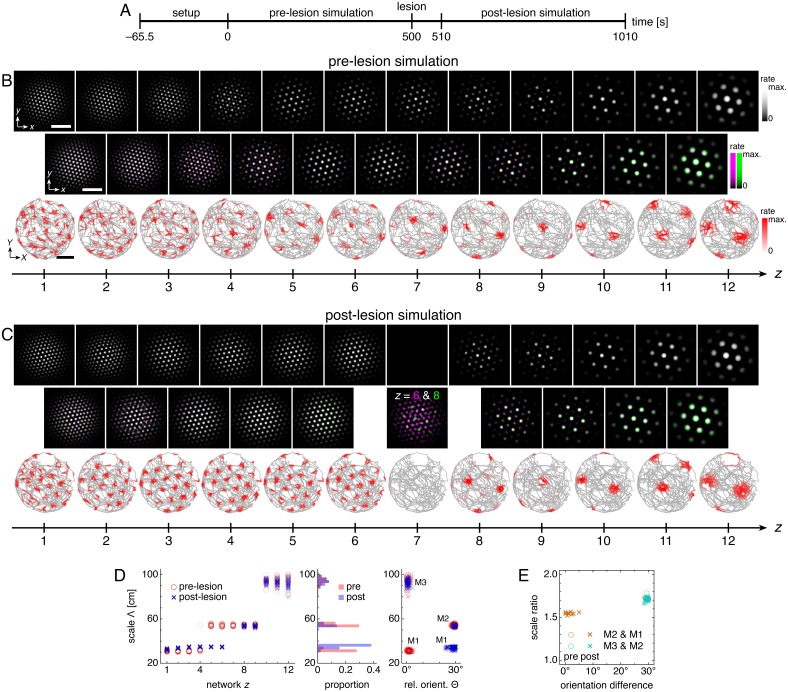
Figure 8. Lesioning a network changes grid scales and orientations of more dorsal networks.
(A) Lesion protocol. The lesion inactivates network z = 7. (B) A representative simulation before the lesion. Top row: network activities at the end of the pre-lesion simulation. Second row: activity overlays between adjacent networks depicted in the top row. In each panel, the network with smaller (larger) z is depicted in magenta (green), so white indicates activity in both networks. Third row: spatial rate map of a single neuron for each z superimposed on the animal’s trajectory. White scale bars, 50 neurons. Black scale bars, 50 cm. (C) Same as B but after the lesion. Spatial rate maps are recorded from the same neurons as in B. (D, E) Data from 10 replicate simulations. (D) Left: spatial grid scales Λ(z) before and after the lesion. Middle: histogram for Λ collected across all networks. Right: spatial orientations Θ relative to the grid cell in the same simulation with largest scale. (E) Spatial scale ratios and orientation differences between adjacent modules. Standard parameter values provided in Table 1.