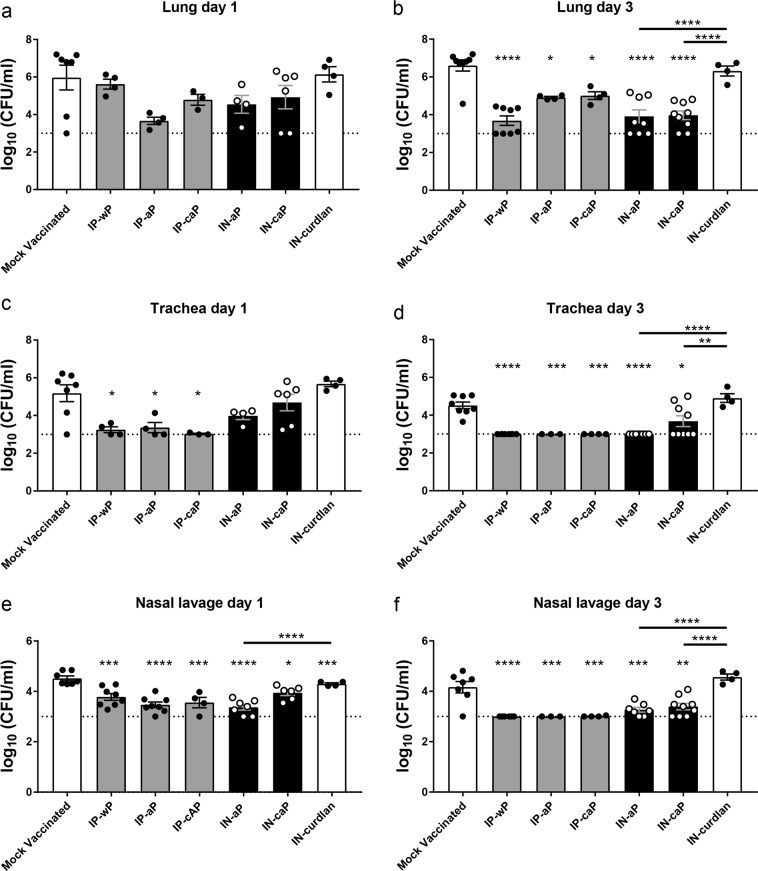
Fig. 7.
Intranasal immunization reduced respiratory B. pertussis bacterial burden. Analysis of bacterial burden was determined at days 1 and 3 pc. Bacteria were quantified by counting of serially diluted CFUs following immunization and challenge. CFU counts were determined from lung homogenate (a, b), trachea homogenate (c, d), and nasal lavage fluid (e, f). Results are mean ± SEM (n = 4–8, with four averaged technical replicates) from two independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test compared to mock vaccinated mice, or between connected columns. The dashed line represents the lower limits of detection due to plating