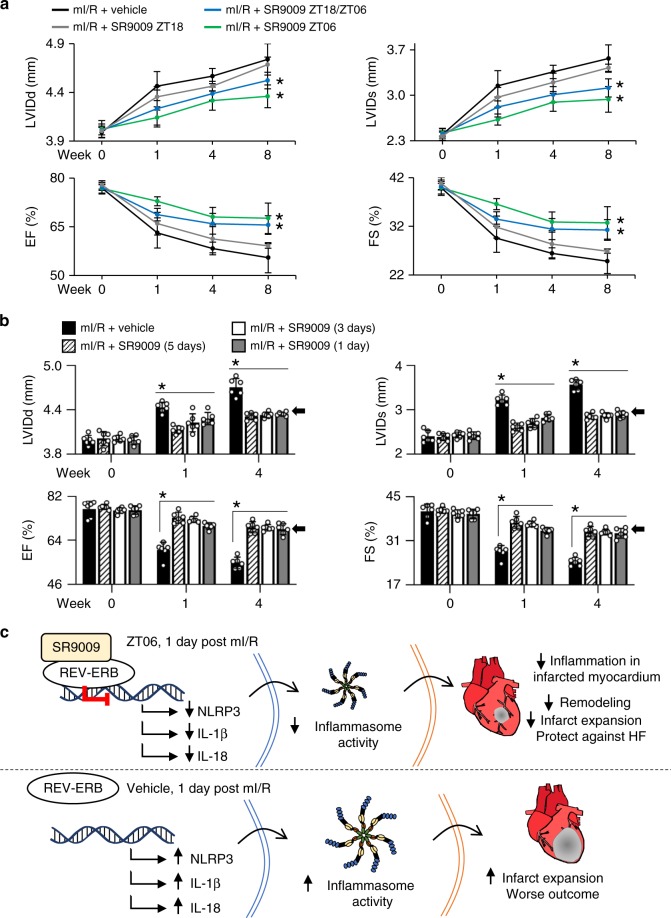
Fig. 5.
Treatment with SR9009 is time-of-day dependent, and treatment for just 1 day leads to improved outcomes post-mI/R. a Mice subjected to mI/R during their sleep time (ZT01-04) or wake time (ZT13-16) were chronotherapeutically treated with SR9009 at time points corresponding to the peak (ZT06) or trough (ZT18) of cardiac REV-ERB expression (see Supplementary Fig. 4). First or subsequent treatments at sleep time (ZT06) were most effective; see Supplementary Table 6 for all pathophysiology values. b Mice were subjected to mI/R (ZT01-04) and treated with SR9009 (ZT06) for 1, 3, or 5 days. Just 1 day of SR9009 treatment was sufficient to benefit outcomes versus vehicle-treated control; see Table 2 for pathophysiology data. c Proposed mechanism for the beneficial effects of targeting REV-ERB post-mI/R. SR9009 enhances REV-ERB repressor activity leading to reduced NLRP3 inflammasome priming and activation in the infarcted myocardium post reperfusion, leading to more efficient repair processes and protecting against HF