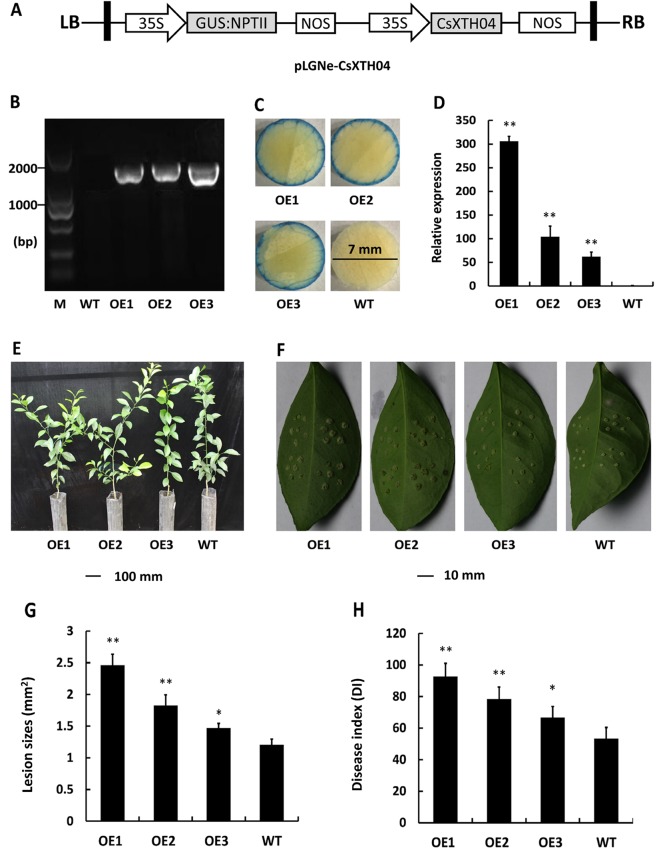
Figure 5.
Characterization and evaluation of CsXTH04 overexpression plants in response to Xcc. (A) Structure of the plasmids for overexpression assays (pLGNe-CsXTH04). LB, left border; RB, right border; 35S, CaMV35S promoter; NOS: terminator. (B) Validation of transgenic plants by PCR. (C) Validation of transgenic plants by GUS assays (leaf disc diameter = 7 mm, staining period = 24 h). (D) Overexpression of CsXTH04 detected by qRT–PCR. (E) Phenotypes of transgenic plants. (F) Disease symptoms on leaves of overexpressed transgenic and WT plants inoculated by Xcc. Sampling and imaging at 10 dpi. Lesion sizes (LSs) (G) and disease index (DI) (H) of each transgenic plant were assessed to evaluate disease resistance. In (D), (G), and (H), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 Student’s t-test. Each value represents the mean ± SD. In (B) to (H), OE1–OE3 indicate overexpression plants; WT, wild type. In (B), M indicates DNA marker. qRT–PCR, quantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction; Xcc, Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri.