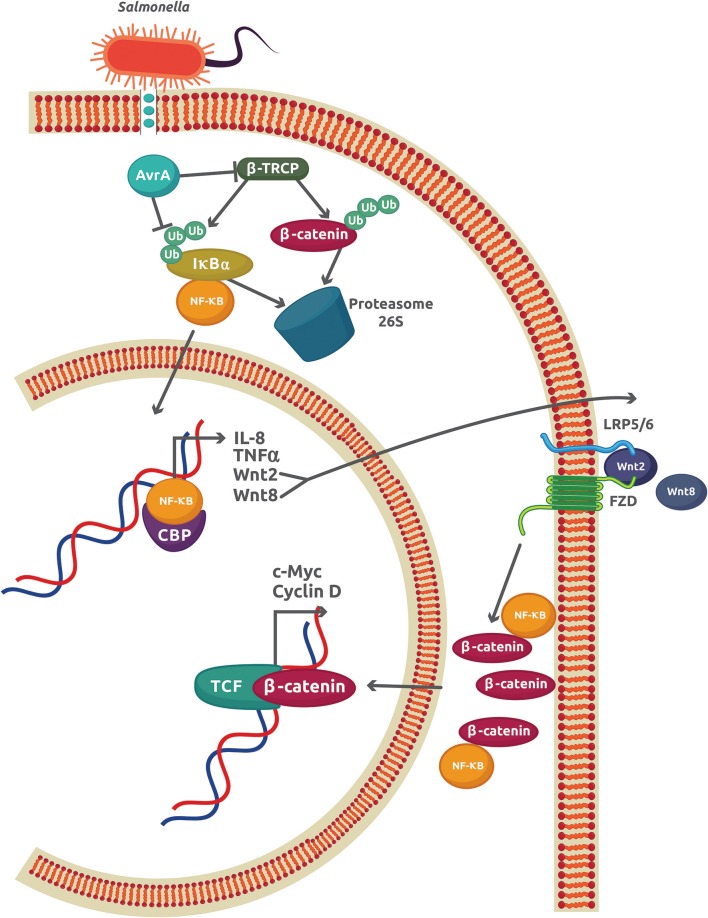
Figure 2.
The AvrA virulence factor from S. enterica sv Typhimurium inhibits the inflammatory response in epithelial cells. The initial inflammatory response promoted by interaction of S. enterica with TLRs leads to an increase in the NF-κB activity and expression of the classical genes, IL-8 and TNFα, and also to Wnt2 and Wnt8. The autocrine effect of Wnt2/8 is to promote the cytoplasmic accumulation of β-catenin. Part of this β-catenin reduces the amount of free NF-κB by forming a complex with the NF-κB p50 subunit. S. enterica injects the virulence factor Avra through a type 3 secretion system. AvrA is also able to both inhibit the activity of β-TRCP and directly deubiquitinate IκBα, which increases the stability of the IκBα-NF-κB cytoplasmic complex and reduces the free NF-κB.