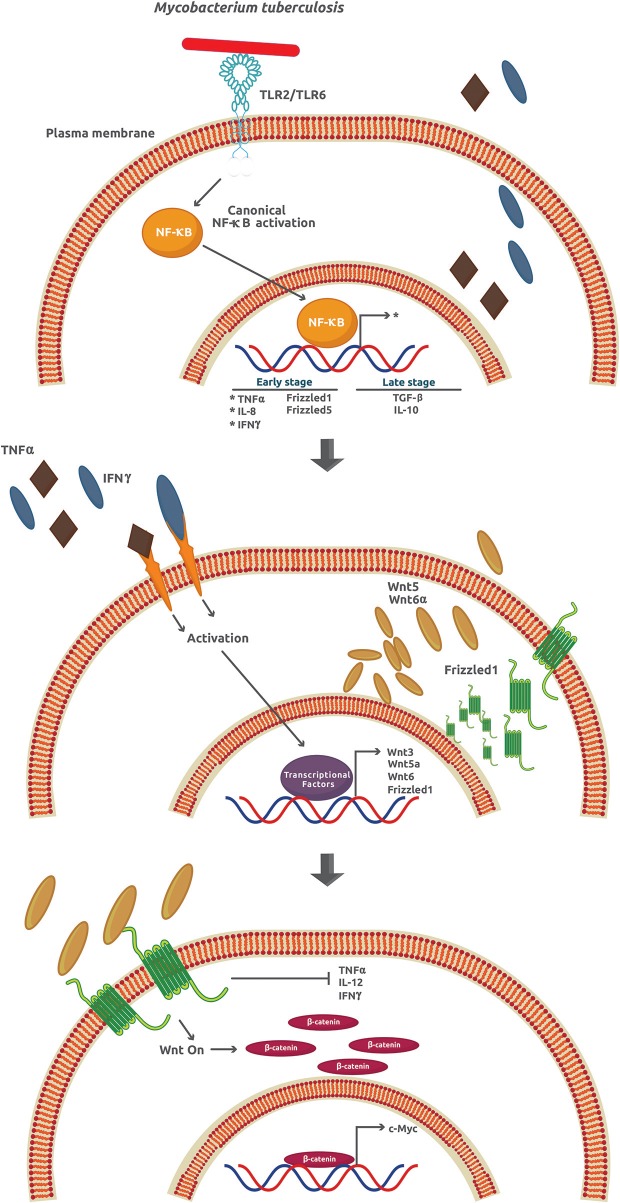
Figure 4.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis activates several signaling pathways that lead to an inflammatory response inhibition. During the early phase of infection, M. tuberculosis induces the expression of TNFα, IL-6, IFNγ, Frizzled1, and Frizzled5. However, at later stages of infection, there is an increase of the anti-inflammatory cytokines TGFβ and IL-10. The secreted TNFα and IFNγ promote the paracrine expression of Wnt3, Wnt5a, Wnt6, and Frizzled1 that in turn activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling.