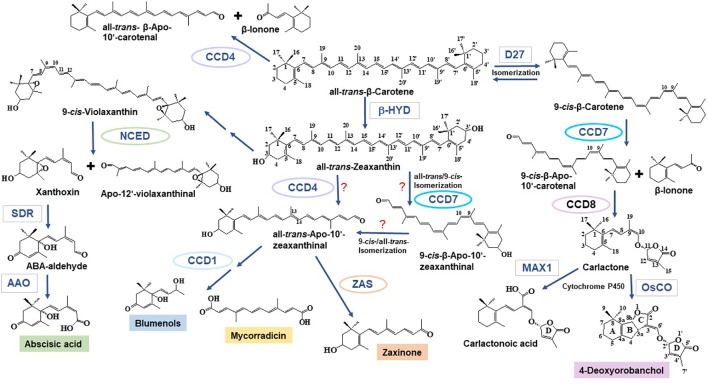
Figure 1.
Formation of apocarotenoids involved in mycorrhization. Nine-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED) enzymes catalyze the cleavage of 9-cis-violaxanthin—formed from all-trans-zeaxanthin through epoxidation and isomerization reactions—and 9’-cis-neoxanthin (not shown) into the ABA precursor xanthoxin and apo-12’-violaxanthinal (or apo-12-neoxanthinal, not shown) (Nambara and Marion-Poll, 2005). Xanthoxin is then further converted to ABA by SDR and AAO. Carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase (CCD) enzymes catalyze a set of different carotenoid and apocarotenoid cleavage reactions. The C27 apocarotenoids β-apo-10’-carotenal and/or β-apo-10’-zeaxanthinal may be formed by CCD4 enzymes that cleave all-trans-bicyclic carotenoids (Bruno et al., 2015; Bruno et al., 2016). CCD7 has been also implicated in the formation of all-trans-β-apo-10’-carotenoids, which include the zaxinone precursor all-trans-β-apo-10’-zeaxanthinal (see below); however, in this case, a cis to trans isomerization must be postulated, as the apo-10’-carotenoids produced by CCD7 enzymes are 9-cis-configured (Alder et al., 2012; Bruno et al., 2014). Several enzymatic studies show that CCD1 enzymes can produce C14 directly from carotenoids or—in a secondary cleavage reaction—from all-trans-β-apo-10’-carotenoids. In the case of mycorrhizal tissues, it is assumed that they use β-apo-10’-carotenoids as substrate to form precursors of mycorradicin and blumenols (structure shown as blumenol C), which accumulate in AM-colonized root and act as symbiosis signal in plant leaves, respectively (Floss et al., 2008b; Walter et al., 2010; Hou et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2018). Following β-carotene isomerization catalyzed by D27, the SL biosynthetic enzyme, CCD7, cleaves 9-cis-β-carotene into 9-cis-β-apo-10’-carotenal and β-ionone. This step is followed by the CCD8-catalyzed conversion of 9-cis-β-apo-10’-carotenal into carlactone. Carlactone, a central intermediate in SL biosynthesis, is further modified by cytochrome P450 enzymes of the 711 clade (i.e., the Arabidopsis MAX1 (Abe et al., 2014), the rice carlactone oxidase (Zhang et al., 2014), which yield canonical, e.g., 4-deoxyorobanchol, and non-canonical, e.g., carlactonoic acid, SLs. Carlactonoic acid is further modified into different products (Alder et al., 2012; Bruno et al., 2014; Al-Babili and Bouwmeester, 2015; Bruno et al., 2017; Abuauf et al., 2018; Jia et al., 2018). ZAS, a recently identified CCD, cleaves apo-10’-zeaxanthinal, yielding the novel signaling molecule, zaxinone (Wang et al., 2019). β-Apo-10’-zeaxanthinal could be formed from zeaxanthin or lutein (not shown) by CCD4 enzymes. Enzymes are surrounded either by ellipses (CCDs) or rectangles (other enzymes). SDR, short chain dehydrogenase reductase; AAO, Abscisic aldehyde oxidase; β-HYD, β-hydroxylase; D27, DWARF27; MAX1, more axillary growth1; OsCO, rice carlactone oxidase, a MAX1 homolog.