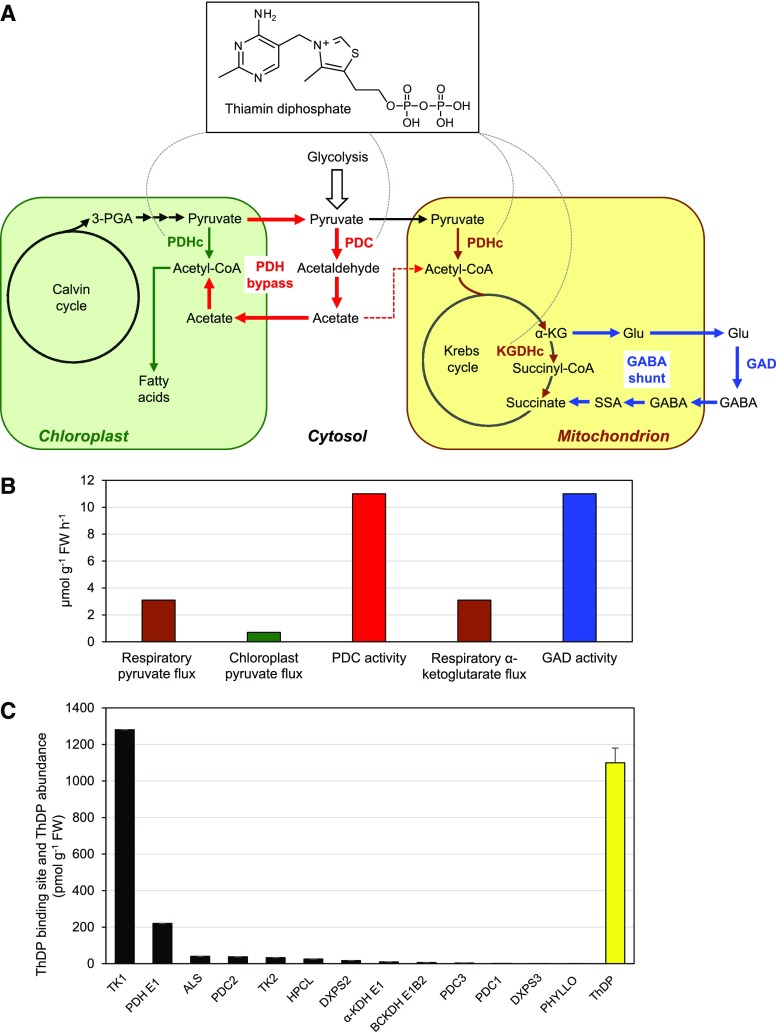
Figure 1.
The PDH bypass, the GABA shunt, and their relationship to ThDP. A, Scheme showing the PDH bypass (red arrows), the GABA shunt (blue arrows), and the α-keto-acid dehydrogenase complexes that they circumvent. The PDHc occurs in mitochondria and chloroplasts; the KGDHc is solely mitochondrial. The dashed red arrow leading from cytosolic acetate to mitochondrial acetyl-CoA denotes an undefined pathway by which acetate is respired (Eastmond et al., 2000). The dashed arcs radiating from the ThDP structure indicate the enzymes in the scheme that are ThDP-dependent. B, Estimated in vivo fluxes through the mitochondrial PDHc, the chloroplast PDHc, and the KGDHc in Arabidopsis leaves compared with the extractable activities of Arabidopsis leaf PDC and GAD. Supporting literature and calculations are given in Supplemental Data. C, Abundance of ThDP binding sites (black bars) and ThDP cofactor (yellow bar) in Arabidopsis leaves, estimated from PaxDb abundance data for ThDP-dependent enzymes, and from ThDP contents taken from three independent articles. The ThDP values are means ± sd. Calculations are detailed in Supplemental Data. FW, fresh weight. Enzyme abbreviations: TK, transketolase; PDH E1, pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit; ALS, acetolactate synthase; HPCL, 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA lyase; DXPS, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-P synthase; α-KDH E1, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase E1 subunit; BCKDH E1, branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase E1 subunit; PHYLLO, MenF/MenD/MenC/MenH fusion enzyme.