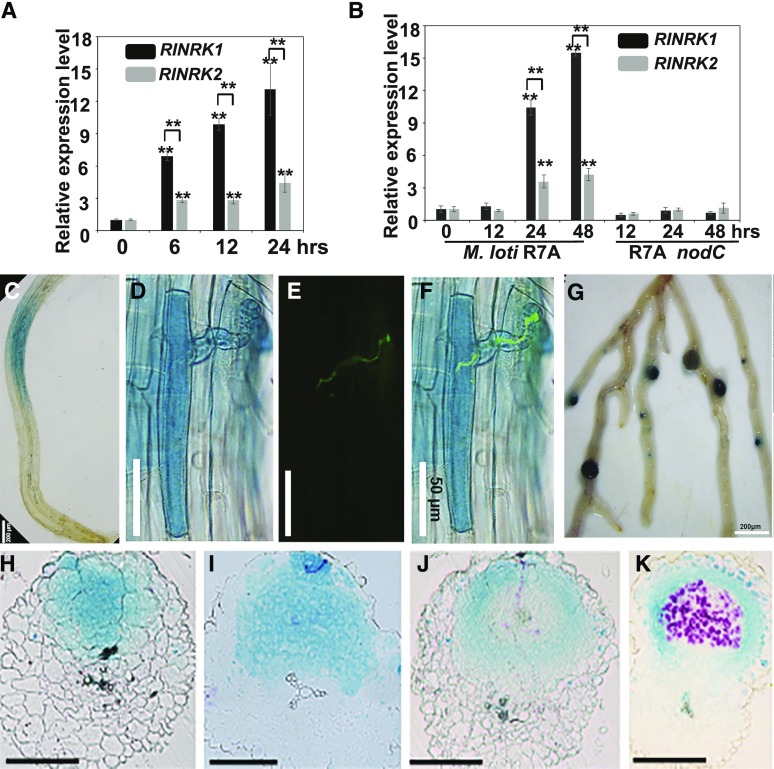
Figure 3.
RINRKs are induced by NFs or M. loti and expression pattern of RINRK1. A and B, RINRK1 and RINRK2 expression in L. japonicus roots measured by RT-qPCR 6, 12, and 24 h after addition of 10 nm M. loti NFs (A) or 12, 24, and 48 h after inoculation with M. loti R7A or M. loti R7A nodC (B). Expression is relative to mock-treated samples and normalized to Ubiquitin. Means and SEs were derived from three biological replicates, and statistically significant differences are shown (**P < 0.01, Student’s t test). C to G, Histochemical localization of GUS activity in A. rhizogenes roots of L. japonicus wild type transformed with proRINRK1:GUS. Transformed hairy roots were analyzed 24 h after NF addition (C; n > 15), and 5 d (D–F) or 14 d (G) after inoculation of M. loti R7A carrying GFP or lacZ. The presence of infection threads was indicated by constitutively expressed GFP in M. loti R7A (E), and the images (D) and (E) were merged in (F). H to K, Sections of nodules indicating RINRK1 expression in whole cell layers of young uninfected nodules (H and I) and in epidermal and nodule parenchyma cells in mature nodules (J and K). The transgenic roots were costained with Magenta-Gal and X-Gluc to visualize M. loti (in purple) and proRINRK1:GUS expression (in blue), respectively, in nodules. Bars = 200 μm (C and G), 50 μm (D–F), and 150 μm (H–L).