Figure 2. Both CENP‐CCR and CENP‐Cmotif bind specifically to the CENP‐A nucleosome, and CENP‐CCR easily competes out CENP‐Cmotif bound to CENP‐A.
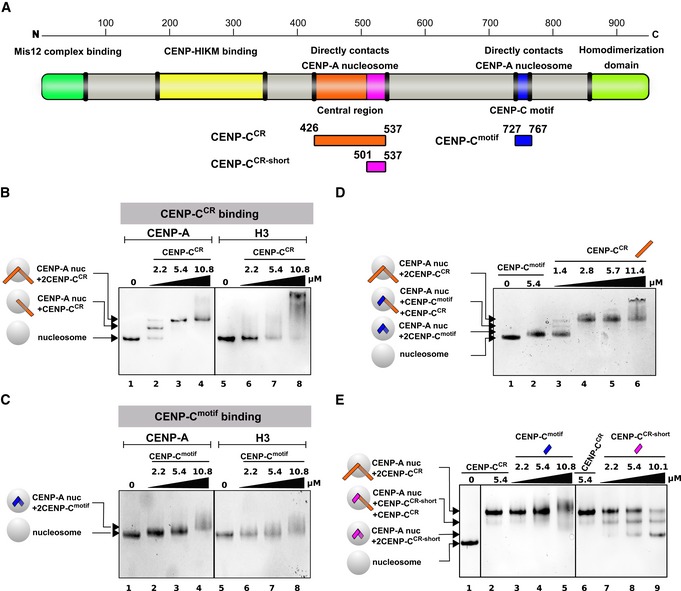
- Schematic diagram of the full‐length CENP‐C protein, indicating parts involved in interactions with other proteins or homo‐dimerization. Constructs used in this study are depicted below the diagram.
- Native PAGE gel stained with Coomassie blue showing complexes formed between CENP‐A or H3 nucleosome and CENP‐CCR. Lane 1: CENP‐A nucleosome, Lanes 2–4: Increasing amounts of CENP‐CCR are added to CENP‐A nucleosome. Generation of a sharp band with slower mobility indicates formation of a specific CENP‐A/CENP‐CCR complex. Lane 5: H3 nucleosome. Lanes 6–8: Increasing amounts of CENP‐CCR are added to H3 nucleosome. Smear on the gel indicates formation of non‐specific H3/CENP‐CCR complexes.
- Same experiment as in (B) using CENP‐Cmotif. Lane 1: CENP‐A nucleosome. Lanes 2–4: Increasing amounts of CENP‐Cmotif are added to CENP‐A nucleosome. Upon binding CENP‐Cmotif, CENP‐A nucleosome migrates slower through the gel. Note only modest change in mobility due to small size of CENP‐Cmotif, comparing to CENP‐CCR in (B). Lane 5: H3 nucleosome. Lanes 6–8: Increasing amounts of CENP‐Cmotif are added to H3 nucleosome. Smear on the gel indicates formation of non‐specific H3/CENP‐Cmotif complexes.
- Native gel showing CENP‐CCR competing out CENP‐Cmotif bound to CENP‐A nucleosome. Lane 1: CENP‐A nucleosome. Lane 2: CENP‐A/CENP‐Cmotif complex. Lane 3–6: Increasing amounts of CENP‐CCR are added to the pre‐formed CENP‐A/CENP‐Cmotif complex. Formation of slower migrating bands indicates that longer CENP‐CCR is replacing shorter CENP‐Cmotif bound to the CENP‐A nucleosome.
- Native gel showing the inability of CENP‐Cmotif to compete out CENP‐CCR bound to CENP‐A nucleosome. Lane 1: CENP‐A nucleosome. Lanes 2 and 6: CENP‐CCR/CENP‐A nucleosome complex. Lanes 3–5: Increasing amounts of CENP‐Cmotif are added to the pre‐formed CENP‐A/CENP‐CCR complex. Formation of smear at high amounts of CENP‐Cmotif added indicates that CENP‐Cmotif, at high concentrations, non‐specifically binds CENP‐A/CENP‐CCR complex rather than replacing bound CENP‐CCR. Lanes 7–9: Increasing amounts of CENP‐CCR‐short are added to the pre‐formed CENP‐A/CENP‐CCR complex. Formation of bands with higher mobility indicates that smaller CENP‐CCR‐short is effectively replacing bigger CENP‐CCR bound to CENP‐A nucleosome.
