Figure 1. Structure and dynamics of SecYEG translocon.
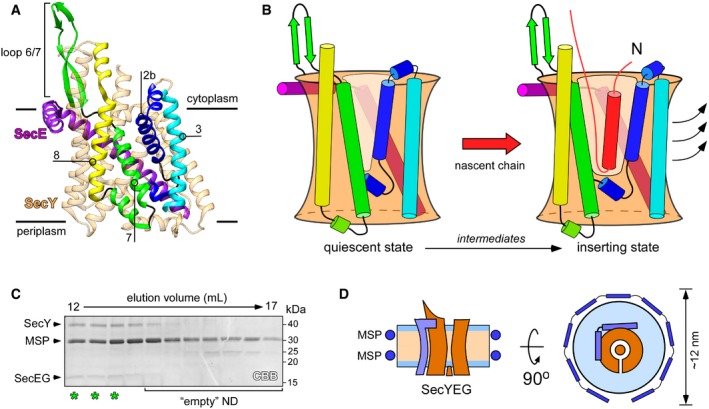
- Structure of quiescent SecYEG of Thermus thermophilus in the lipid cubic phase (PDB ID: 5AWW). TMHs 2b, 3, 7, and 8 of the lateral gate, as well as the proximate loop 6/7 involved in ribosome binding are indicated. The non‐essential SecG subunit is omitted for clarity.
- Model of the SecY lateral gate opening upon inserting a nascent chain (red) in the lipid bilayer. The color‐coding of SecYE TMHs is as in panel (A). In the presence of the completely inserted and folded nascent chain, TMHs 2b and 3 of the N‐terminal domain of SecY are displaced (arrows) thus opening a broad passage for the nascent TMH toward the lipid moiety.
- SDS–PAGE of SecYEG‐ND sample after size‐exclusion chromatography. Asterisks indicate translocon‐enriched fractions used for forming the RNC FtsQ:SecYEG‐ND complex. Lipid‐loaded “empty” nanodiscs elute at larger volumes and so can be separated.
- Schematic drawing of a SecYEG‐ND particle. Lateral dimensions of the nanodisc should be appropriate to accommodate a single SecYEG with surroundings lipids, thus mimicking the naturally occurring environment.
