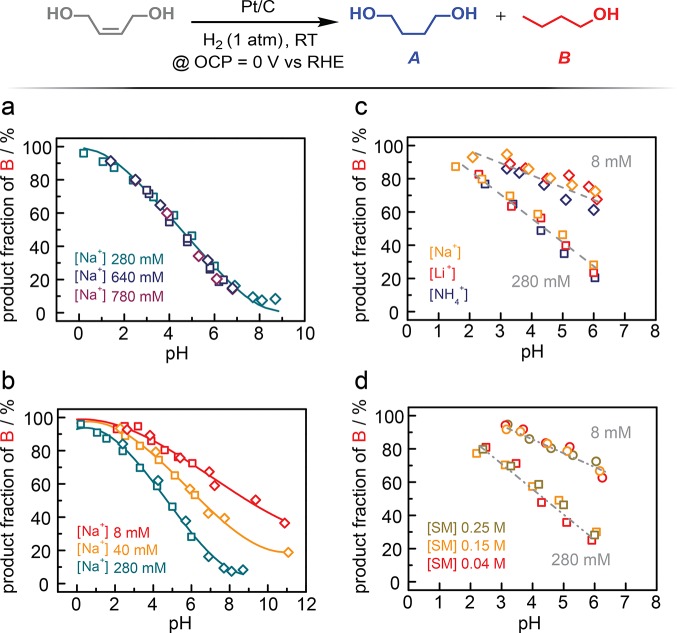
Figure 2.
Product fraction of n-butanol, B (in %), at approximately 30% total conversion for Pt/C-catalyzed H2 addition to cis-2-butene-1,4-diol as a function of electrolyte conditions. (a) pH dependence of B fraction under high ionic strength (I) conditions in the presence of 280 (green, I = 0.4 M), 640 (blue, I = 0.8 M), and 780 mM Na+ (purple, I = 1.0 M). (b) pH dependence of B fraction under low ionic strength conditions in the presence of 40 (orange, I = 0.05 M) and 8 mM Na+ (red, I = 0.01 M). For panels (a) and (b), data were collected in the presence of citrate (square) and phosphate (diamond) counteranions. (c) pH dependence of B fraction with varying cation species, Na+ (orange), Li+ (red), and NH4+ (blue) with 280 (square, I = 0.4 M) and 8 mM (diamond, I = 0.01 M) of each cation. (d) pH dependence of B fraction with varying substrate (SM = starting material) concentrations, 0.25 (green), 0.15 (orange), and 0.04 M (red), under varying ionic strength electrolytes containing 280 (square, I = 0.4 M) and 8 mM Na+ (circle, I = 0.01 M). All data were collected at the open-circuit potential, ∼0 V vs RHE.