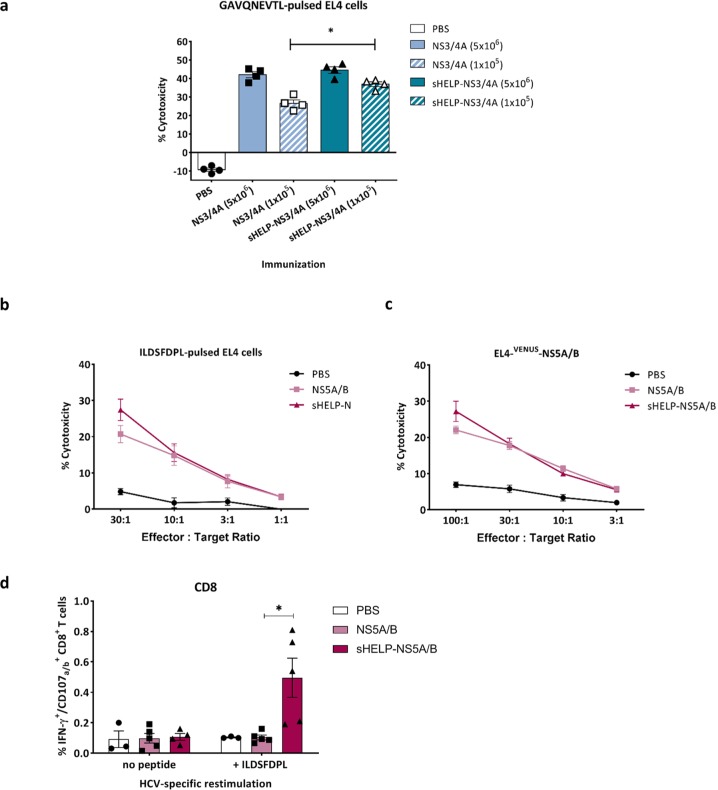
Figure 4.
Induction of HCV-specific CTLs upon SFV immunizations. Mice were primed and boosted intramuscularly with (a) 5 × 106 or 105 SFV-NS3/4A or SFV-sHELP-NS3/4A infectious particles, (b) to (d) 5 × 106 SFV-NS5A/B or SFV-sHELP-NS5A/B infectious particles, or PBS at a 2 week interval. Mice were sacrificed 10 days after the last immunization, and splenocytes were isolated for an in vitro cytotoxicity assay (a) to (c) and intracellular cytokine staining using flow cytometry (d). (a) Isolated splenocytes were cultured with Hepa1-6VenusnsPs cells at a ratio of 25:1. After a 7 day culture, splenocytes were co-cultured for 4 h with 51Cr labeled target EL4 cells pulsed with GAVQNEVTL peptide at 25:1 ratio. (b) and (c) Isolated splenocytes were cultured with Hepa1-6VenusNS5A/B cells at a ratio of 25:1. After a 7 day culture, splenocytes were co-cultured for 4 h with 51Cr labeled target EL4 cells pulsed with ILDSFDPL peptide or EL4-VENUS-NS5A/B at the indicated E:T ratios. (d) Splenocytes were stimulated with ILDSFDPL for 4 h and subjected to surface and intracellular cytokine staining. The frequencies of IFN–γ+CD107a/b+ within the CD8+ T cells are shown. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3–5). *p < 0.05.