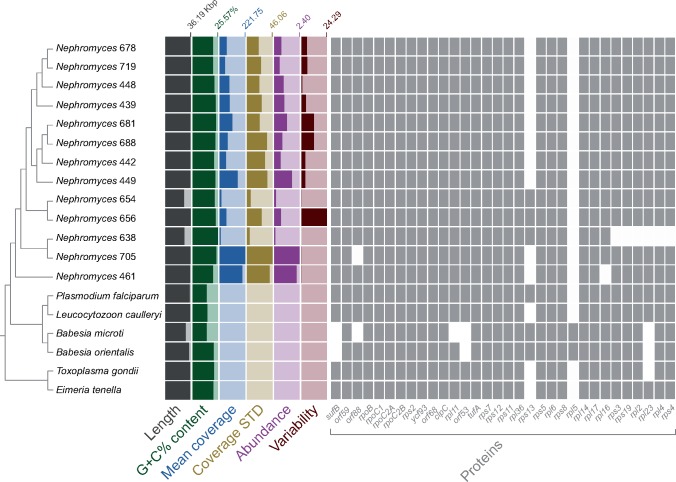
Fig. 2.
—The Nephromyces clade (Nephromycida) is diverse and here comprises at least 13 distinct apicoplast genomes found in a metagenome derived from the renal sac of a single individual of the molgulid tunicate host, Molgula occidentalis. Each apicoplast genome is found at different abundances in the metagenome. The genomes show differences in gene content, G+C% content, and sequence divergence (see branch lengths in supplementary fig. S4A, Supplementary Material online). The guide cladogram is derived from the phylogram in supplementary figure S5, Supplementary Material online. The predicted genes orf59 and orf88 might be rps18 and rpl19, respectively, based on remote similarities to these genes in the GenBank nr database. Genome features were calculated in Anvi’o v4. The apicoplast genomes of Nephromyces 654 (26.24 kb) and 656 (26.78 kb) could not be circularized and appear as smaller than all others because they lack one or both rRNA-gene operons, respectively. Mean coverage: average depth of coverage across contig. Coverage STD: the standard deviation of coverage values for a given contig. Abundance: mean coverage of a contig divided by that sample’s overall mean coverage. Variability: number of reported single-nucleotide variants per kilo base pair.