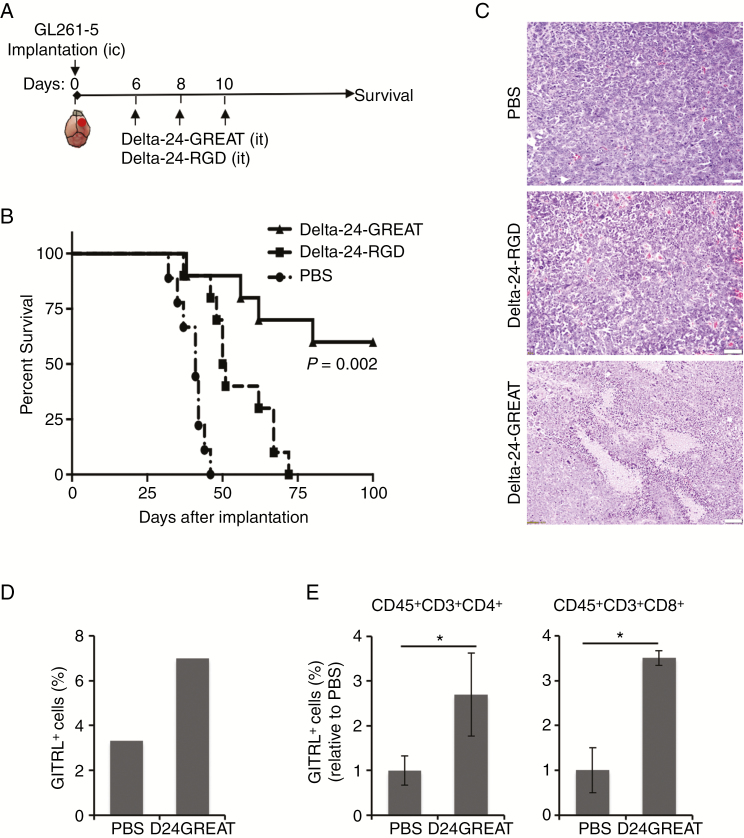
Figure 2.
In vivo effect of Delta-24-GREAT. (A) Schema of the preclinical study. GL261-5 cells (5 × 104 cells/5 µL) were implanted intracranially (ic) in the right caudate nucleus of C57BL/6 mice using a guide-screw system. Delta-24-GREAT or Delta-24-RGD (5 × 107 pfu; 5 µL) was intratumorally (it) injected on day 6, 8, and 10 after tumor cell implantation. PBS was used as control. (B) Survival plots of experiment described in (A) showed prolonged survival with long-term survivors (>100 days) of Delta-24-GREAT-treated mice. (n = 10, Delta-24-RGD and Delta-24-GREAT; n = 9, PBS). P = .002 (log-rank test; Delta-24-GREAT vs Delta-24-RGD). (C) Histopathological examination of hematoxylin and eosin stained sections of tumors of mice that showed signs of disease, and displayed high cellularity. Delta-24-GREAT-treated mice showed increased areas of necrosis. Scale bar = 100 μm. (D) Expression of mGITRL was analyzed by FACS 15 days after tumor implantation, and 5 days after the last viral dose. Data are represented as percentage of positive cells (3 brains were pooled for analysis). (E) Expression of mGITR in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was analyzed by FACS 15 days after tumor implantation. Data are represented as mean ± SD, relative to PBS values (equal to 1) (n = 3). *P < .05, Student’s t-test, double sided.