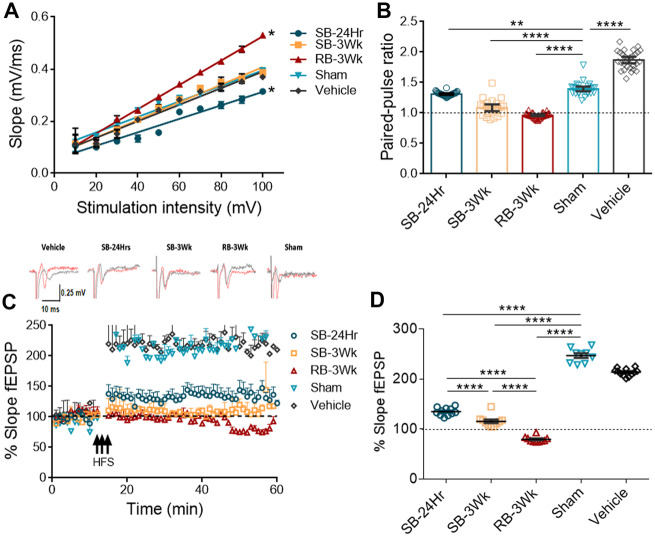
Figure 4.
Tau oligomers derived from brains exposed to single versus repetitive TBI impair LTP to different magnitudes with the sample from the repetitive blast showing the most impairment. Hippocampal slices (350 µm thickness) were treated with the oligomers for 1 h at 50nM. (A) The input–output curve shows the RB-3Wk oligomers increase basal neuronal transmission (R2 = 0.9922, *P < 0.0001) whereas the SB-24Hr oligomers decrease it (R2 = 0.9484, *P < 0.0001) in comparison to vehicle control (R2 = 0.9743). (B) Paired-pulse ratios results show that all the oligomers impaired facilitation in comparison to sham-treated groups, and RB-3Wk oligomers completely abolished it. (C) LTP impairment profiles show that RB-3Wk and SB-3Wk abolish LTP whereas SB-24Hr partially impairs LTP in comparison to sham oligomers. Representative traces before (black) and after (red) LTP are shown above LTP plot. (D) The last 10 min of LTP were analysed separately. Results show that LTP is significantly impaired with the single blast oligomers. The repetitive blast oligomers show a synaptic depression effect. Linear regression analysis indicating significantly different slopes from vehicle treatment in A (****P < 0.00001, **P < 0.001). (one-way ANOVA was used in B and D; post hoc comparison: adjusted using Sidak correction. n = 6 slices).