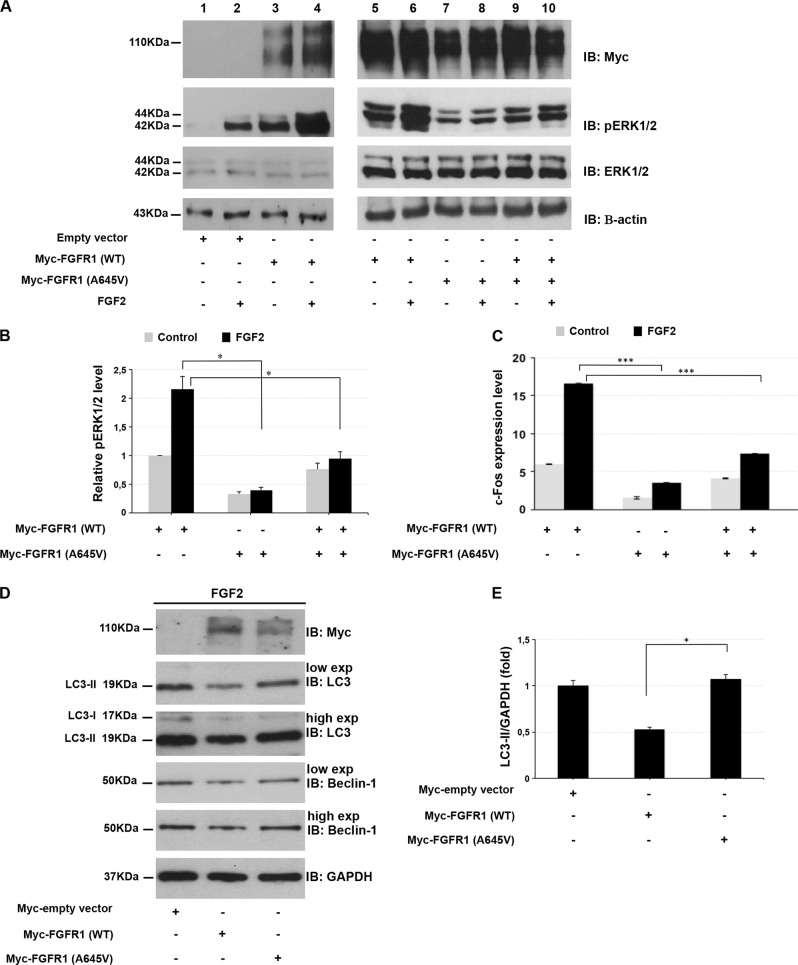
Fig. 2.
Ala645Val FGFR1 impairs ERK1/2 signaling pathway and autophagy flux. a HEK293 cells were transfected with empty vector (lanes 1, 2), wild-type FGFR1 (lanes 3–6) and Ala645Val FGFR1-expressing plasmids (lanes 7, 8) or wild-type plus Ala645Val FGFR1 plasmids (lanes 9, 10). At 24 h after transfection, cells were grown in serum-free medium for 24 h, and then incubated in the absence (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9) or presence of 1 nM FGF2 (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10) for 15 min. After incubation with FGF2, the phosphorylated ERK1/2 was analyzed by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using indicated antibodies. Actin was used as loading control. b Quantitative analysis of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in cells transfected with indicated vectors. Protein levels were quantified by densitometry. The relative ERK1/2 phosphorylation level in cells transfected with the vector expressing wild-type FGFR1 was set as 1. Bar represents the average of three independent experiments and scale bars represent standard errors. *P < 0.05. c qPCR was performed to measure the c-Fos endogenous expression in HEK293 cells transfected with indicated plasmids and cultured in the absence or presence of 0.5 nM FGF2 for 1 h. The relative c-Fos expression in cells transfected with the empty vector was set as 1. Scale bars represent standard errors. ***P < 0.01. d Whole protein lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with empty vector, wild-type or Ala645Val FGFR1-expressing plasmids and cultured in the absence or presence of 25 ng/ml FGF2 for 2 h, were separated on 12% SDS-gel and subjected to immunoblotting with LC3 and Beclin-1 antibodies (low and high exposure). The autophagy flux was monitored by the conversion of LC3-I to its lipidated form, LC3-II. GAPDH was used as loading control. The same lysates were separated on 7.5% SDS-gel for immunoblotting with anti-Myc. e Quantification of LC3-II levels. Graph shows averages calculated on two different experiments and scale bars represent standard errors. *P < 0.05