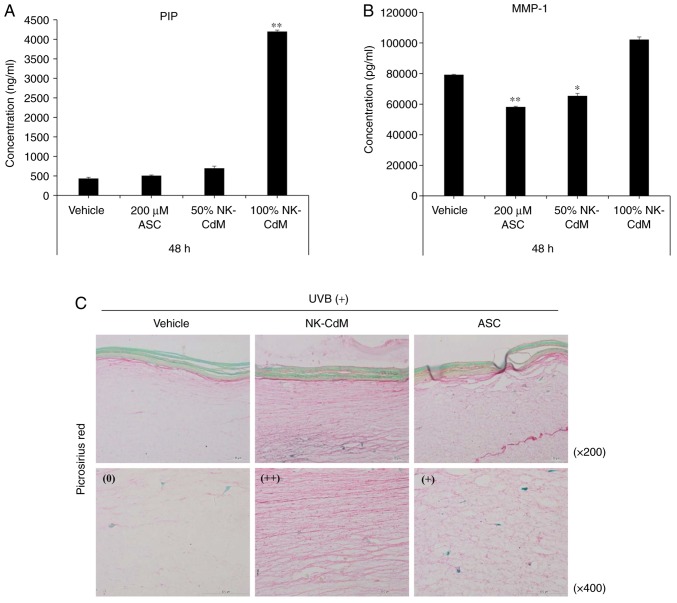
Figure 5.
Inhibitory effects of NK-CdM on UV-B-induced collagen degradation in a 3D reconstructed human full skin model. Tissues were irradiated with UV-B (125 mJ/cm2), and further incubated with vehicle (PBS containing 0.1% DMSO) and NK-CdM (50 and 100%) and ascorbic acid (200 μM) at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. The levels of (A) type I procollagen and (B) MMP-1 in the culture media were measured using a commercially available ELISA kit, as described in the Methods. The data are the mean ± standard deviation values of three individual experiments. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. UV-B-irradiated vehicle control. (C) To confirm the inhibitory effects of NK-CdM on UV-B-induced collagen degradation in skin model, the Keraskin-FT™ was stained with PSR, which stains collagen red. The visual assessments of collagen degradation represent the average of the scores in each PSR staining intensity category (++ indicates pronounced findings, + moderate findings, and 0 no/scant findings) identified for each score. NK-CdM, natural killer cell conditioned medium; NHDF, neonatal human dermal fibroblasts; UV, ultraviolet; PSR, picrosirius red; ASC, ascorbic acid; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PIP, pro-collagen type 1 C-peptide.