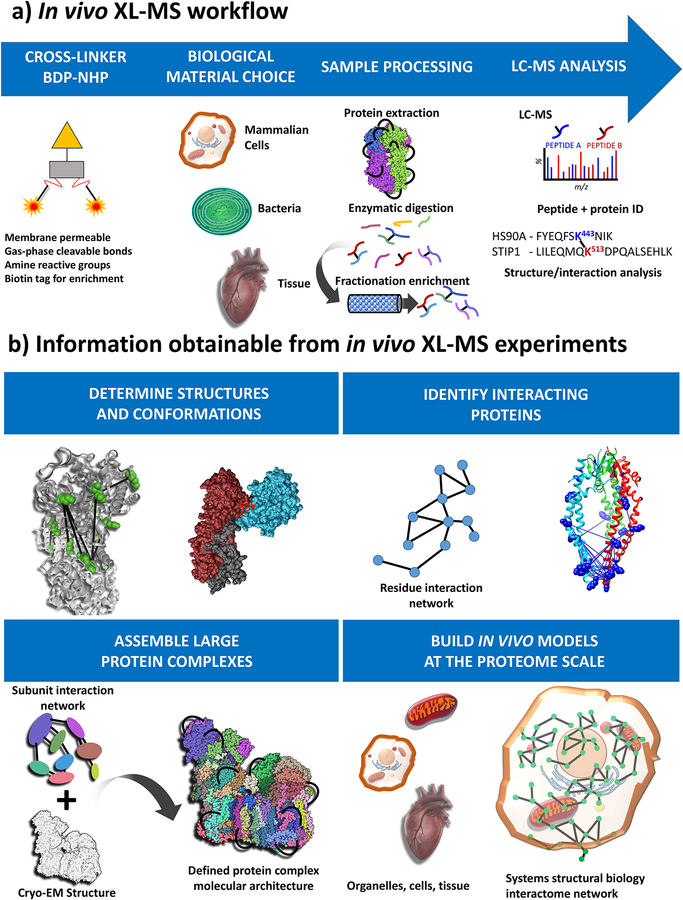
Figure 2.
Experimental overview of in vivo XL-MS. a) General workflow includes applying cross-linker (BDP-NHP) to a biological material of choice, which can include mammalian cells, bacterial cells, or animal tissue samples. This is followed by protein extraction, enzymatic digestion, fractionation and enrichment of cross-linked peptide pairs. Cross-linked peptide pairs are identified by LC-MS analysis. b) Types of information resulting from in vivo XL-MS experiments include protein structural and conformational information. XL-MS data can be integrated with data from Cryo-EM or other structural biology techniques to assemble structural models for large protein complexes. Identification of interacting proteins can be used to assemble proteome scale interactome maps for cross-linked systems including organelles, cells and tissues.