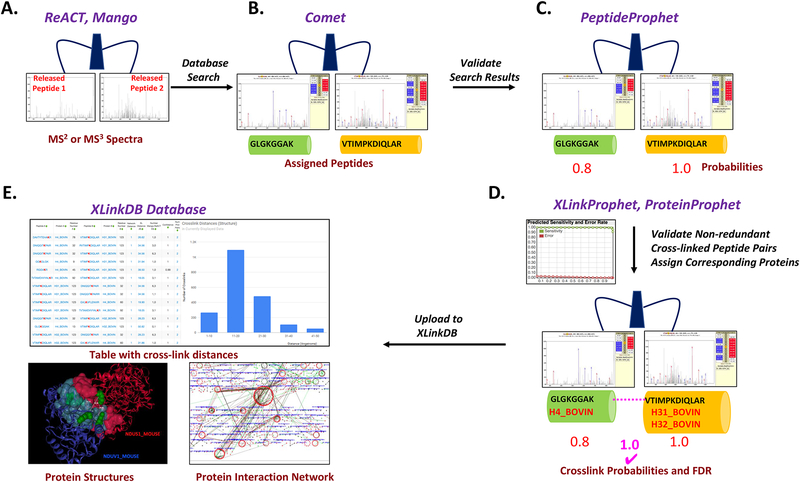
Figure 3.
Data analysis workflow. a) Mass spectra containing the mass of the intact cross-linked peptide pair, masses of the individual released peptides and fragment ions of the released peptides are acquired by ReACT or Mango methods. b) Database search is carried out by Comet to assign peptide sequences to the mass spectra. c) PeptideProphet is run on the Comet search results to assign probabilities to individual peptide sequences. d) XLinkProphet is run to validate the cross-linked peptide pair and corresponding proteins by assigning a cross-link probability and estimation of FDR. e) Validated results are uploaded into the XLinkDB database where a table of the identified cross-linked peptide pairs can be viewed in a table or interaction network format. Cross-links are mapped to existing PDB structures and homology based structural models and distance information for each cross-link is generated. Resulting protein structures with cross-links mapped onto them can be viewed.