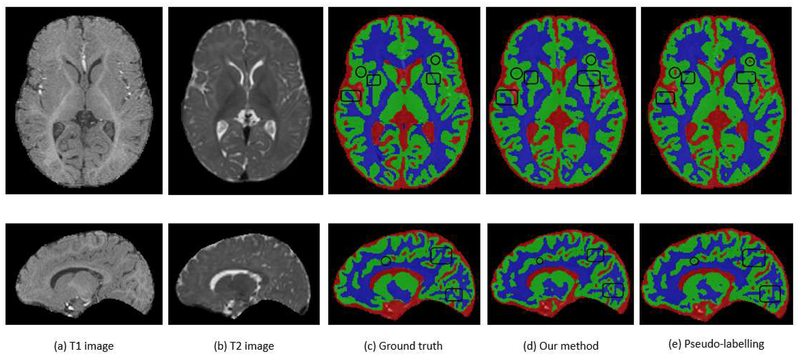
Fig. 12.
Results of (d) our model (SSLDEC) on a case from the isointense infant brain MRI segmentation challenge (iSeg), compared to (c) the ground truth (manual segmentation) and (e) a pseudo-labelling technique. Original T1- and T2-weighted MRI images of this case are also displayed in (a) and (b) which show the difficulty in distinguishing WM and GM due to their isointensity appearance at this age. These slices were extracted from image 6 on the iSeg dataset, after training models on one fifth of 2 images only (images 1 and 2 in the iSeg dataset). These results show that the pseudo-labelling technique includes several CSF zones, which are not present in the ground truth or in the results of our semi-supervised technique (black circles). Overall, SSLDEC also seems to be more accurate in separating gray and white matters as several WM zones are correctly linked by our SSLDEC model, whereas not by the pseudo-labelling technique (black rectangles). There are areas in which the pseudo-labelling segmentation seems more similar to ground truth than SSLDEC segmentation, but the overall results show that SSLDEC outperformed pseudo-labelling in this case and other cases, as confirmed by average Dice scores obtained and reported in Figures 9, 10, and 11. The average Dice score (over the three classes) of the SSLDEC model for this case was 89.3%, while it was 87.5% for the pseudo-labelling technique.