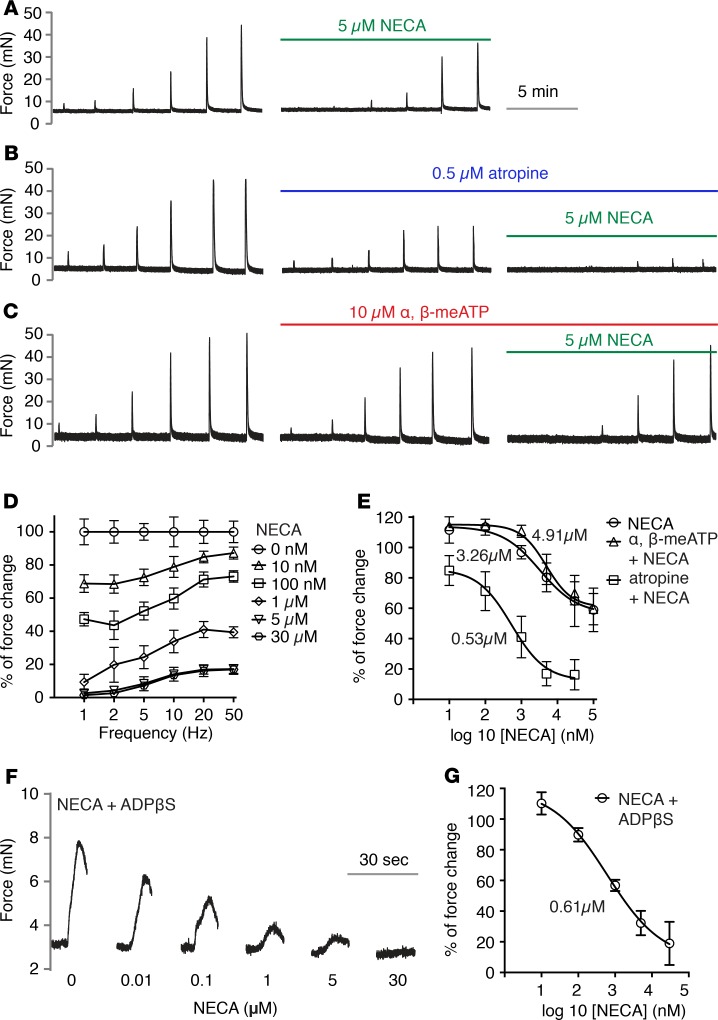
Figure 1. Activation of adenosine receptor inhibits bladder smooth muscle purinergic contraction.
Bladder smooth muscle (BSM) strips were stimulated by electrical field stimulation (EFS) at indicated frequencies in increasing order (D: x-axis). (A) Representative traces of BSM contraction in response to EFS stimulation, which is partially inhibited by 10 minutes NECA pretreatment (n = 10). The EFS frequencies used are shown on the x-axis in D. (B) Pretreatment with atropine inhibits muscarinic contraction, and the remaining purinergic contraction (or atropine resistant) is fully inhibited by NECA (n = 8). (C) When ATP-mediated purinergic contraction is inhibited by α,β-meATP desensitization, the remaining muscarinic contraction is not sensitive to NECA activation of adenosine receptor (n = 8). Force changes were normalized to control and shown as percentages. (D) Quantitation of data shown in B. (E) Nonlinear regression of A, B, and C, which shows the dose response under 20-Hz EFS stimulation, and the corresponding IC50. (F) Representative traces of BSM contraction in response to ADPβS (n = 7), which is dose-dependently inhibited by NECA pretreatment. Quantitation shown in G. Data are shown as mean ± SD, dose response was analyzed by 1-way ANOVA, P < 0.05