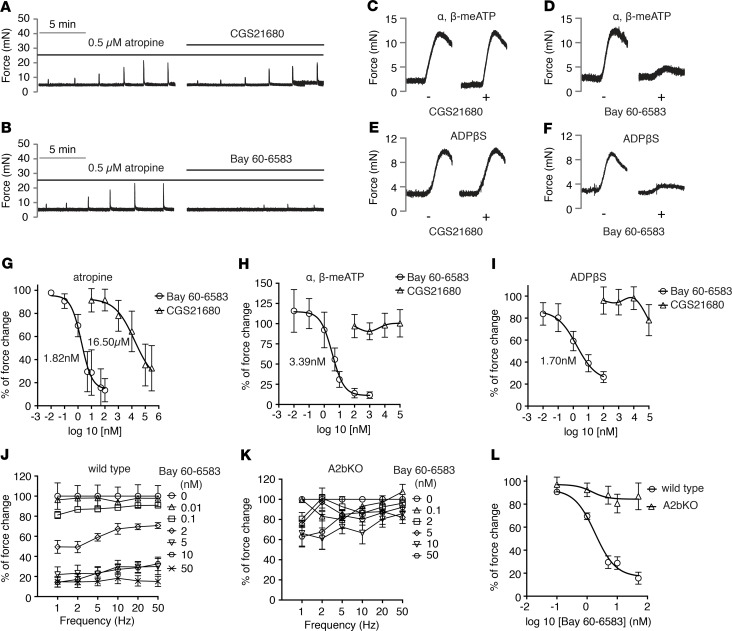
Figure 2. Adenosine A2b receptor is the major receptor in mediating inhibition of bladder smooth muscle purinergic contraction.
(A) Representative traces of bladder smooth muscle (BSM) purinergic contraction in response to electrical field stimulation (EFS) stimulation, which is insensitive to A2a receptor activation by CGS21680 (n = 7). (B) Representative traces of BSM purinergic contraction in response to EFS stimulation, which can be fully inhibited by A2b receptor activation by Bay 60-6583 (n = 13). (C) Representative traces of BSM contraction in response to α,β-meATP stimulation, which the CGS21680 pretreatment does not inhibit (n = 7). (D) Pretreatment with Bay 60-6583 inhibits α,β-meATP stimulated BSM contraction (n = 7). (E) Representative traces of BSM contraction in response to ADPβS stimulation, which CGS21680 pretreatment does not inhibit (n = 8). (F) Pretreatment with Bay 60-6583 inhibits ADPβS stimulated BSM contraction (n = 7). (G) quantitated data of A and B. (H) Quantitated data of C and D. (I) Quantitated data of E and F. (J) Dose-dependent inhibition by Bay 60-6583 on BSM purinergic contraction (atropine pretreatment) in response to EFS stimulation (n = 13). This inhibition is abolished in A2b-KO BSM as shown in K (n = 7). (L) Nonlinear regression of J and K.