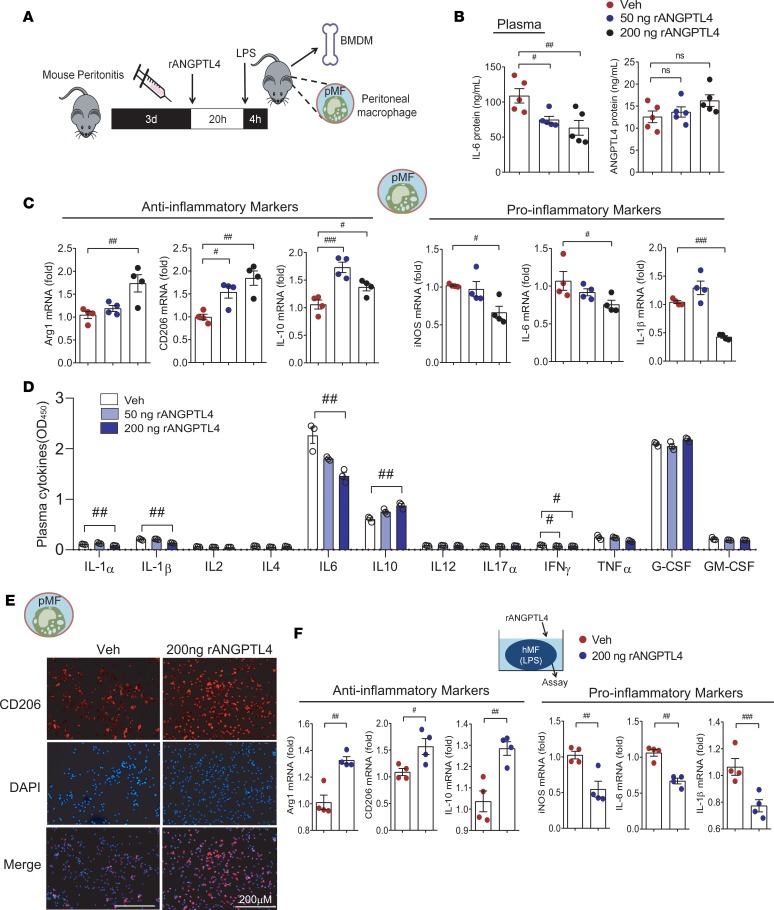
Figure 6. Recombinant ANGPTL4 suppresses the activation of peritoneal macrophages and BMDMs.
(A) Veh or recombinant ANGPTL4 protein (50 or 200 ng) was injected to mice with peritonitis. Peritoneal macrophages (pMFs) and BMDMs were used to examine the antiinflammatory effect of ANGPTL4 treatment in a peritonitis mouse model. (B) Circulating IL-6 and ANGPTL4 were measured in the Veh group, 50-ng ANGPTL4 group, and 200-ng ANGPTL4 group. n = 5 for each group. (C) Inflammation-related genes of peritoneal macrophages were assessed. n = 4. (D) Inflammatory mediators in the plasma were analyzed by multiplex ELISA. n = 3. (E) Expression of CD206 was assessed by immunofluorescence staining in peritoneal macrophages. (F) Inflammation-related genes were assessed and the antiinflammatory phenotype was observed in BMDMs isolated from the ANGPTL4 group. n = 4. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001 (by Student’s t test or 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparisons test).