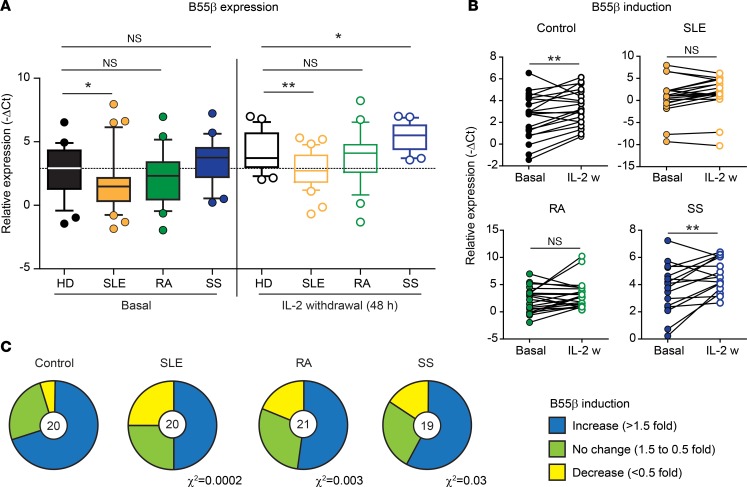
Figure 1. Expression and induction of B55β is impaired in T cells from patients with systemic autoimmune diseases.
(A) Abundance of the B55β transcript was quantified in activated T cell blasts from healthy donors (HDs) and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), before (basal) and 48 hours after IL-2 withdrawal. Data are presented as median and quartiles (25th to 75th). Whiskers represent the 10th and 90th percentiles, and outliers are indicated by circles (HD basal vs. SLE basal P = 0.024; HD 48 hours vs. SLE 48 hours P = 0.002; HD 48 hours vs. SS 48 hours P = 0.012; Mann-Whitney U test) (HD n = 25; SLE n = 32; RA n = 28; SS n = 21). (B) Induction of B55β induced by IL-2 withdrawal (24 hours) is shown (HD basal vs. 24 hours P = 0.005; SLE basal vs. 24 hours P = 0.066; RA basal vs. 24 hours P = 0.064; SS basal vs. 24 hours P = 0.007, paired two-tailed t test) (HD n = 20; SLE n = 20; RA n = 21; SS n = 16). (C) The proportion of controls and patients with increased B55β expression after IL-2 withdrawal is shown. The number in the pie chart indicates the number of controls or patients included in the analysis. Under the corresponding pie chart, χ2 of the distribution ratio (increase/no change/decrease) of HDs versus each autoimmune disease is indicated. IL-2 w, IL-2 withdrawal.