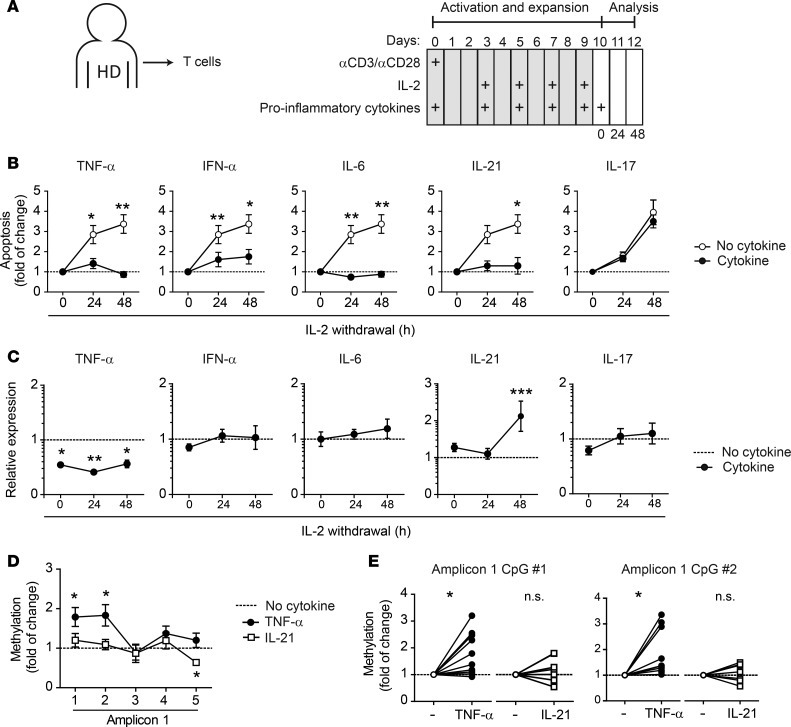
Figure 7. TNF-α induces PPP2R2B methylation, abolishes B55β expression, and impairs CWID in healthy T cells.
(A) T cells from HDs were activated and expanded in the presence of IL-2 for 10 days. In addition to IL-2, at days 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8, the indicated cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-α, IL-6, IL-21, or IL-17) were added to the culture. At day 10, cells were counted, washed, and replated in the absence of IL-2 and proinflammatory cytokines. (B) Apoptosis (annexin V+ SYTOX Orange−) was quantified before (0 hours) and after IL-2 withdrawal (n = 3–6). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test. (C) Expression of B55β was determined (qPCR) before and after (24 and 48 hours) IL-2 withdrawal. Results were normalized against ACTB (Ct) and then against cells expanded in the presence of IL-2 but in the absence of other cytokines (ΔΔCt). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; 2-way ANOVA. (D) Methylation of the CpG dinucleotides from Amp 1 was determined by pyrosequencing in cells expanded in IL-2 (dotted line) and compared with the CpG DNA methylation of the same cells expanded in the presence of TNF-α or IL-21 (n = 8–11). *P < 0.05, paired two-tailed t test. (E) The relative change in methylation status of single CpG dinucleotides in response to TNF-α and IL-21 is shown (n = 8–11). *P < 0.05, paired two-tailed t test.