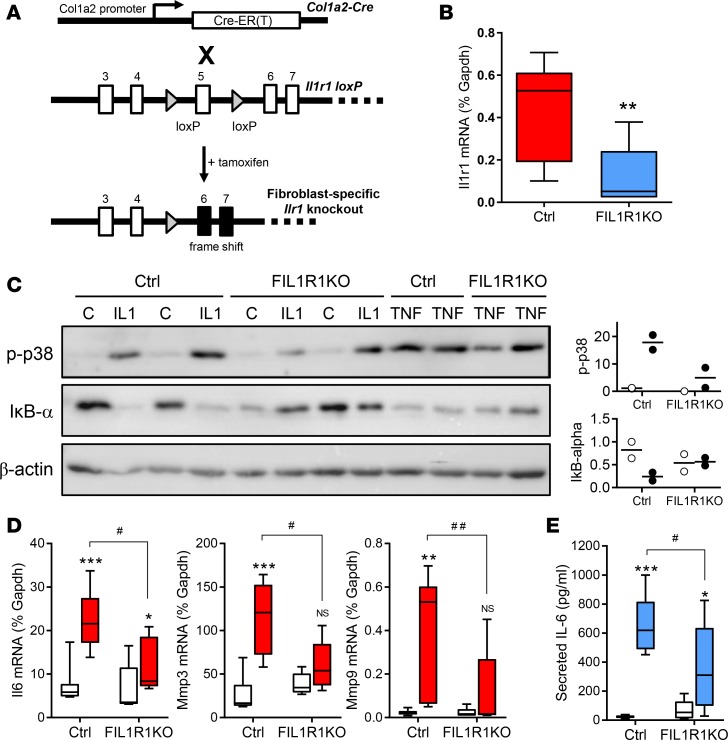
Figure 4. Effect of tamoxifen-induced fibroblast-specific IL-1R1 knockdown on cardiac fibroblast responses to IL-1.
(A) Schematic showing loxP-targeted Cre-mediated deletion of exon 5 within the IL-1 receptor-1 gene, Il1r1. (B–E) Fibroblast cultures were established from hearts of Cre-negative (Ctrl; n = 7) and Cre-positive (fibroblast-specific IL-1 receptor 1 KO [FIL1R1KO]; n = 5) hemizygous Il1r1fl/– mice 6 weeks after tamoxifen injection. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of basal Il1r1 mRNA expression in cardiac fibroblasts from Ctrl and FIL1R1KO mice. **P < 0.01 for effect of KO (unpaired t test). (C) Cardiac fibroblasts with different genotypes were exposed to vehicle (control, C), IL-1α (IL-1), or TNF-α (TNF) for 30 minutes before immunoblotting to measure activation of p38 MAP kinase (phosphorylation; p-p38) or activation of IκB-α (proteasome-mediated degradation). β-Actin, loading control. Plots to the right depict densitometric analysis relative to β-actin normalized to lane 1 for control (white symbols) or IL-1 treatment (colored symbols). n = 2. (D and E) Cardiac fibroblasts were treated with vehicle (white boxes) or 1 ng/ml IL-1α (colored boxes) for 6 hours before measuring mRNA levels of Il6, Mmp3, and Mmp9 by qRT-PCR (D), and IL-6 secretion by ELISA (E). ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, NS, not significant for effect of IL-1; ##P < 0.01; #P < 0.05 for effect of IL-1R1 KO (2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc).