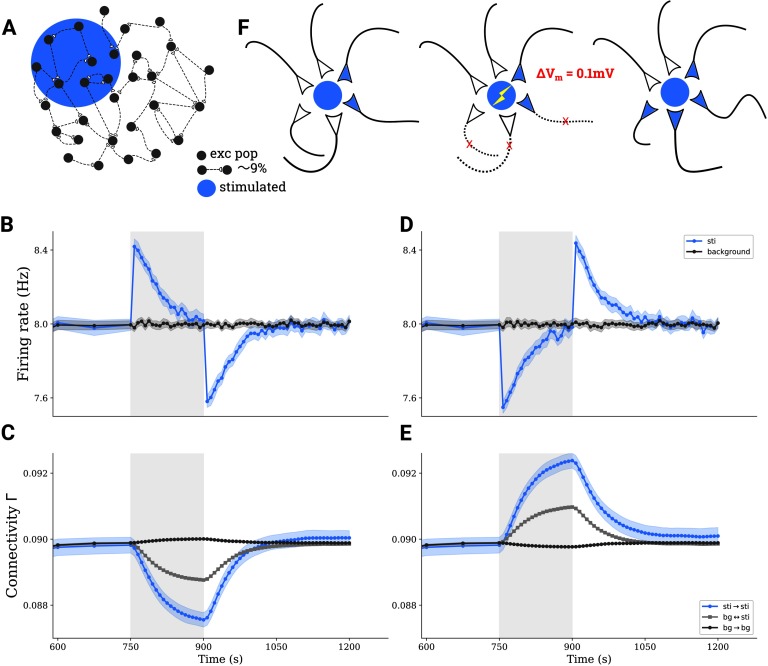
Figure 2. .
tDCS triggers the formation of cell assemblies. (A) A subgroup comprising 10% of all excitatory neurons in a larger network is stimulated by tDCS. (B) Average firing rate of directly stimulated (blue) and unstimulated (gray) excitatory neurons before, during, and after applying a depolarizing stimulus. (C) Average connectivity among stimulated neurons (blue), among unstimulated neurons (dark gray), and between neurons belonging to different groups (light gray) upon depolarizing stimulation. (D–E) Similar to (B–C), but for a hyperpolarizing stimulus. Shaded areas on (B–E) indicate the stimulation period. (F) Illustration explaining the process of structural plasticity that happened after a depolarizing tDCS. The stimulation triggers the removal of interpopulation synapses, and accelerates the growth of synapses among stimulated neurons, leading to the formation of cell assemblies.