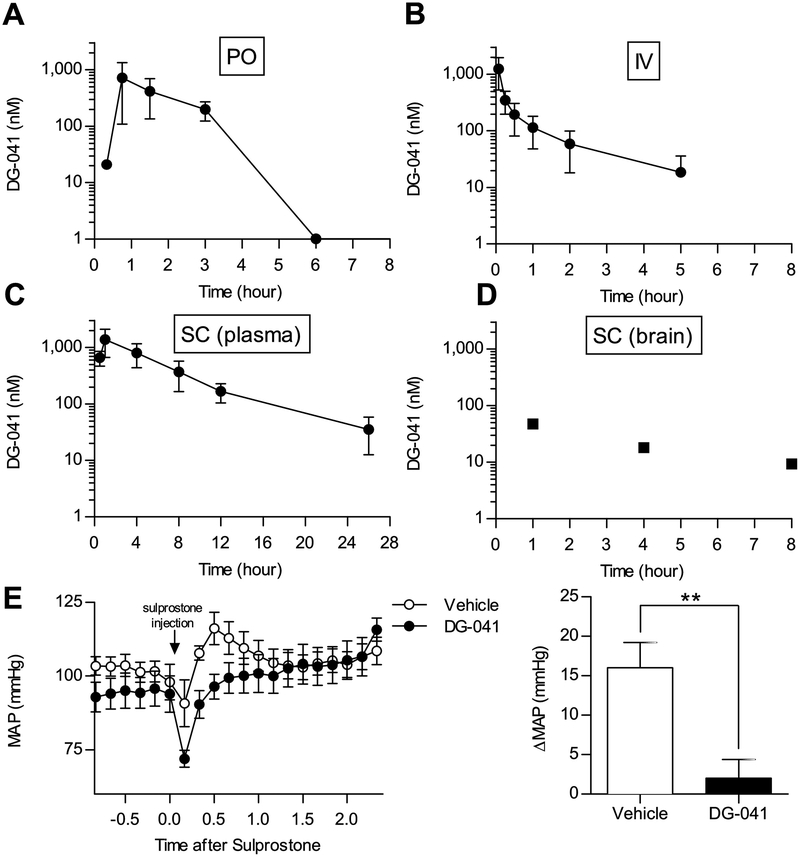
Figure 2. Plasma concentration-time profile of DG-041 following oral gavage, intravenous injection, and subcutaneous administration.
A. 30 mg/kg DG-041 was administered to mice by oral gavage (per os, PO). Plasma DG-041 concentrations were measured from cardiac puncture blood. By six hours after gavage, plasma DG-041 concentrations were below the detectable limit. N = 2 mice per time point. B. 2 mg/kg DG-041 was administered by intravenous injection (IV). Plasma DG-041 concentrations were measured from saphenous vein or cardiac puncture blood at the indicated times. N = 5. C. 20 mg/kg DG-041 was administered to mice by subcutaneous injection (SC). Plasma DG-041 concentrations were measured from saphenous vein or cardiac puncture blood at the indicated times. N = 4–6. D. Brain DG-041 concentrations were measured from mice administered DG-041 via SC injection and euthanized at the indicated time. E. Vehicle or 20 mg/kg DG-041was administered by SC injection two hours before internal carotid blood pressure measurements. DG-041 treatment blocked the sulprostone-evoked rise in mean arterial pressure (MAP). N=5 each. For A–C values are expressed as mean ± StDev, for D each data point is representative of one mouse, for E values are expressed as mean ± SEM.